Technologies and applications in additive manufacture of metallic materials
P. Alvarez, F. Garciandia And Or. Gurmendi.
Introduction
The technologies of additive manufacture, additive manufacturing in English, define like the processes of union of materials to create objects, usually layer to layer, from data 3D of a model, of opposite form to the technicians of manufacture sustractiva [1]. These technologies allow the direct manufacture of objects 3D from data or models CAD (Computer Assisted Design).
In the actuality, these technologies allow to manufacture pieces 100% functional with a high value added and constitute a group of emergent technologies that are turning into serious competitors of the processes of mechanised and conformed traditional. This type of technologies are entering of an increasing way in sectors such as the biomédico, aeronautics, automotive sector, mould and matricería and increasingly in the manufacture of products of general consumption.
Main advantages of the technologies of additive manufacture
- Reduction of the time of launching to the market because of the rapidity of the process. Can reduce drastically many of the current phases of launching and validation, as well as flexibilizar his adaptation to the demands in constant change of the market.
- Personalización Of products with a total flexibility in the design and construction. Can produce pieces of practically any form and without almost geometrical limitations. A clear example is the manufacture of implants or prosthesis adapted to the peculiarities of each patient.
- Maximum saving of material. It deletes the waste of material in shape of shaving of mechanised… Exist study where concludes that it is possible to reduce until in 40% the volume of material in the rough [3].
- Do not require useful, moulds neither coin. The pieces produce directly of a model CAD 3D with total absence of human errors in production and can manufacture unitary series without hardly extra costs.
- Produce pieces totally functional and without porosidad residual.
- Manufacture of enclosed structures with freedom of design. It is possible to manufacture pieces with a big complexity of form, with internal channels or reticular structures lightened.
- Possibility to develop products multimaterial, ergonomic or with several integrated mechanisms in a same piece.
The here presented work is precisely headed to analyse and reach these challenges. The advance on the state of the art roots in the definition of the conditions of the dust and of the process (parameters, strategies of manufacture) that allow to avoid the apparition of defects, optimise the density of the pieces manufactured and of his superficial condition and precision.
Fits to signal that at present they exist more than 11.500 patents and applications published on the processes of additive manufacture. Every year they publish more than 1.400 new patents that cover all the facets of the technology including: processes, material and software; diverse applications in medicine, moulds…
Process of selective fusion by laser (SLM)
The process of selective fusion by means of laser, in groins selective laser melting or SLM, is a process of additive manufacture developed recently for metallic materials [4] [5] [6]. The process describes in detail in the Ref. [6]. It bases in the fusion by means of the action of a laser of metallic dust predepositado in layers very fine and uniforms on a platform of work; the process repeats layer to layer until completing the piece. The laser generates in each layer the outline of the piece to build melting the dust. The platform descends along the axis z after finalising each layer an equal distance to the thickness of the layer work (usually between 20 and 50 micras). The processes of application and fusion repeat of successive form until they complete all the layers that constitute the final piece.
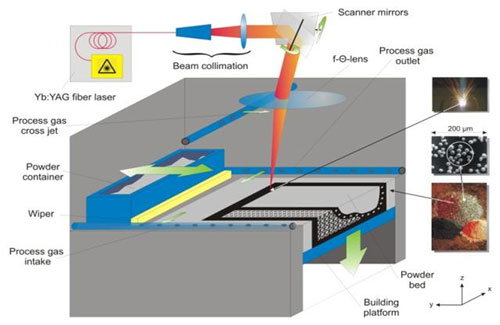
Appears 1: Description the process SLM.
In the technology SLM uses a laser like source of power to melt the dust. A lot of the apt metallic materials for this process are susceptible to the oxidation. By this reason the process SLM carries out in enclosed cameras and usually in protective atmospheres (no oxidants). It is usual to work with alloys of titanium or cobalt-chromium in inert atmospheres of argon.
In the actuality exist distinct commercial marks of equipment SLM. Between them the most notable are Electro Optical Systems (EOS), Realizer GmbH, Renishaw and SLM Solutions GmbH, the two last arisen of MTT Machines [6]. The American company Concept Laser commercialises also this technology with the alternative name of Laser Cusing, although it treats of the same technology. Although the range of materials procesable can vary in function of the characteristics of each team, to day of today can process a big variety of metallic materials between which include stainless steels, steels of tool (H13), alloys of titanium (TiAl6V4 and TiAl6Nb7), alloys of cobalt chromium, alloys of aluminium (AlSi12Mg and AlSi10Mg), alloys of bronze and alloys of nickel (INC625 and INC718).
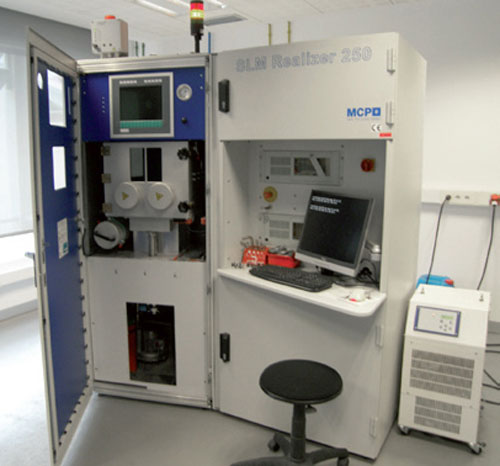

Appears 2: Equipment SLM Realizer 250 of IK4 Lortek.
Applications SLM
In this section show some real examples of pieces and components manufactured by means of SLM in the installations of IK4 Lortek. The components manufactured describe by sectors with the aim to illustrate the capacities and potential applications of the process SLM.
1. Sector biomédico
The medical implants are one of the niches of market more important of the technology SLM. To the equal that the human body, treats of personalised and only pieces. The technology SLM has a big number of advantages in this application between which stand out: the possibility of manufacture of complex and personalised forms, the immediacy in the development of a solution (from a tomography of the zone to reconstruct can design to measure an implant), the reduction of the time and of the surgical complications (can adjust the implant in models before the operation on moulds or skeletons manufactured in polymer from the zone to reconstruct) and the possibility of manufacture of light and gradual structures with a greater compatibility biomecánica, comfort and osteointegración.
IK4 Lortek has worked during the last years in the development of implants and prosthesis maxilofaciales (crowns and dental bridges, reconstruction of jaw), for traumotología (knee, hip) and neurocirugía (cranial implants and of corporectomía). The works realizar have carried out with distinct medical groups of the hospital of Basurto. For the manufacture of these implants has worked with alloys cobalt-chromium, titanium and stainless steel.


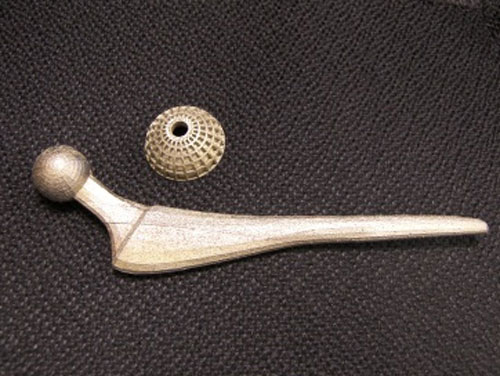
Appears 3: Crowns and dental bridges, implants of column and implant of hip manufactured by IK4 Lortek.
To part of the own implants and prosthesis, the manufacture of instrumental surgical is another of the applications of the technology SLM. In the following Figure includes a detail of guides of cutting and plates of fixation developed for an intervention of surgery maxilofacial reconstructiva in IK4 Lortek.
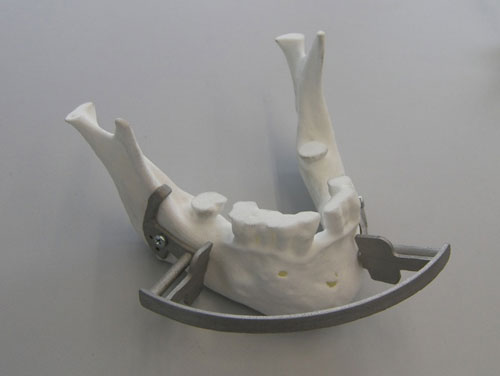
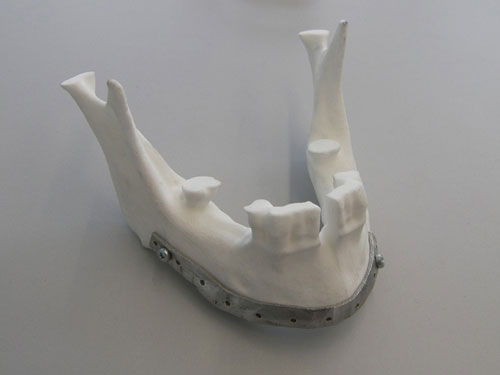
Appears 4: Guide of cutting and fixation for surgery maxilofacial manufactured by IK4 Lortek.
2. Sector mould and matricería
The freedom of design that offers the technology SLM can apply to the manufacture of insertos and moulds. The main aim of the moulds of injection and colada is to ensure a suitable cooling of the piece. This cooling depends on the transfer of heat between the metal melted and the mould. To optimise this cooling can use components manufactured by means of SLM with channels of internal refrigeration that discurran near of the surface. The most usual concept is the manufacture of insertos that plant on blocks of mould prefrabicados. The utilisation of these insertos provides a transfer of heat homogénea (avoids the overheating of parts of the mould), improves the superficial quality of the pieces injected and reduces considerably the cycles of injection.
IK4 Lortek has worked in the development of these insertos for moulds of injection of polymers and aluminium.

Appears 5: Insertos for moulds of injection manufactured by IK4 Lortek.
3. aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing sectors and automotive sector
The technology SLM allows to manufacture reticular structures or of lattice so much with external leather as without leather. This type of structures provide an enormous potential to achieve an aligeramiento structural but up to now was complicated to manufacture them by means of conventional processes. However, the possibilities that offers the technology SLM are applying of a way increasingly patent in sectors where the reduction of weight and the increase of the relation resistance in front of weight suppose an advantage.
In particular in the aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing sector, this technology is supposing a true revolution and are achieving important reductions of the weight and of the costs of production. IK4 Lortek has applied this technology for the manufacture of components of instrumentation and motors of aviation in superaleaciones basic Nickel of the type INC718 [8] and titanium (TiAl6V4). In these applications besides has the advantage of the reduction of the volume of material of necessary game and of the reduction of the consumption of fuel.
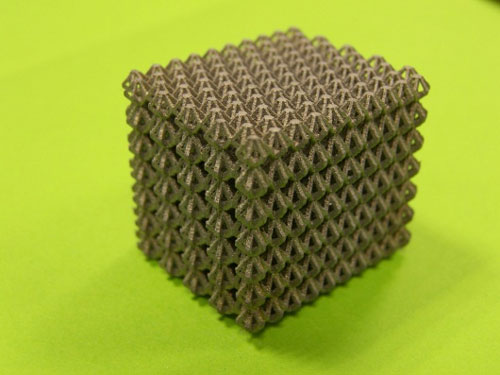
Appears 6: Detail of reticular structures with and without leather manufactured by IK4 Lortek.
The sector of automotive sector is another sector where are identifying applications and components that can manufacture by means of SLM and that they can arrive to integrate other functionalities like acoustic isolation, vibrations…
4. Sector industry of the science
Finally it fits to signal that the industry of the science is a market that sues leading solutions and technologically advanced. The technology SLM Is applying increasingly to the development of components whose manufacture by means of conventional technologies is impossible. With this technology is giving answer to the needs of design, precision and functionality expected for this type of components.

Appears 7: Detail of a component for ITER manufactured by IK4 Lortek.
Conclusions
The technologies of additive manufacture in general and SLM in particular, are going back very attractor trucks for sectors in which they already are entered like the biomédico, aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing, automotive sector or mould and matricería. In this work have presented several examples of pieces manufactured by means of the technology SLM for these sectors. It is to expect that because of the inherent advantages of this process and to the developments that are carrying out, the number of applications grow of exponential way in these sectors and in other new substituting partly to the processes of conventional manufacture.
References
[1] ASTM F2792-10 “Standard Terminology for Additive Manufacturing Technologies”, www.astm.org: ASTM International.
[3] G. Levy, «The role and future of the Laser Technology in the Additive Manufacturing environingingment, » Physics Procedia, vol. 5, pp. 65-80, 2010.
[4] J. Kruth, «Material Incress Manufacturing by Rapid Prototying Techniques, » CIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology, vol. 40, pp. 603-614, 1991.
[5] J. P. Kruth, G. Levy, F. Klocke And T. Childs, «Consolidation phenomena in laser and powder-bed based layered manufacturing, » CIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology, vol. 56, pp. 730-759, 2007.
[6] T. Wohlers, Wohlers Report 2012 Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing State of the Industry, Fort Collins, Colorado: Wohlers Associates, 2012.
[7] [On-line]. Available: http://www.merlin-project.eu/project/index.jsp.
[8] To. Gibson, D. Rosen And B. Stucker, Additve Manufacturing Technologies: Rapid prototyping to Direct Digital Manufacturing", Springer, 2010.