La fabricación aditiva y la BIEMH
Lo que hoy ya todo el mundo conoce como fabricación aditiva se refiere a una tecnología que comenzó en Estados Unidos hace 20 años y que actualmente está logrando sus primeros éxitos. Se trata de la fabricación rápida de piezas partiendo de datos digitales. Avanza a un ritmo vertiginoso que, tras comenzar como una fórmula de fabricación rápida de prototipos, ha pasado a ser también una alternativa rentable para la fabricación de utillaje y, más recientemente, a una opción con un alto potencial en la fabricación directa digital (piezas de uso final, en series cortas). En el origen de su éxito están las limitaciones de la fabricación mediante métodos convencionales en lo que se refiere al tamaño del lote a fabricar (¿Para qué fabricar en serie si no hay demanda para ello?) y a la complejidad geométrica del componente. Pero también hay que tener en cuenta que ahora la sociedad exige una fabricación medioambientalmente responsable y sostenible.
Conceptualmente, la fabricación aditiva describe la tecnología en general y se utiliza cuando se hace referencia a aplicaciones industriales de fabricación de componentes y con equipos profesionales e industriales de altas prestaciones. Existen otros términos, siendo los más conocidos ‘prototipado rápido’ o ‘impresión 3D’, en función del alcance del modelo y el tipo de máquina aditiva empleada. En su favor juegan factores determinantes. Por ejemplo, la posibilidad de imprimir un producto en cualquier parte del mundo a partir de un simple archivo informático, abre todo un mundo de posibilidades. Además, se trata de un proceso que, frente a otras alternativas tradicionales de fabricación, supone grandes ahorros económicos y de tiempo. A todo ello hay que sumar que ya han caducado las patentes de dos líderes del mercado como son Stratasys y 3D Systems, por lo que se está produciendo un 'boom' mundial de nuevos agentes que quieren entrar en este sector.

Capa sobre capa
De forma simplificada, la manufactura aditiva consiste en manipular material a escala micrométrica y depositarlo generalmente capa a capa, para crear objetos a partir de datos 3D de un modelo, de forma opuesta a las técnicas de fabricación sustractiva. Dentro de este ámbito general los procesos pueden ser de lo más variado: laminación o LOM (empleo de capas de diferentes materiales), fotolitografía o estereolitografía (uso de luz UV como proceso básico de solidificación), fusión o sinterización selectiva por láser (uso de un haz de láser y electrones para la consolidación del material), polyjet (se inyectan capas de fotopolímero líquido en una bandeja y se cura al instante mediante luz UV) y modelado o deposición fundida-FDM (deposición de hilo fundido capa a capa, de termoplásticos, ABS, como material básico).
Por otro lado, las técnicas de fabricación aditiva confieren grandes ventajas competitivas debido a su adaptación a la complejidad geométrica y a la personalización del diseño de la pieza a fabricar. Según los sectores de aplicación también puede conseguirse: productos aligerados, productos multimaterial, productos ergonómicos, series cortas de producción, reducción de errores de montaje y sus costes asociados, reducción de costes de inversión en utillaje, combinación de distintos procesos de fabricación, optimización en la utilización de material, fabricación más sostenible.
Sin embargo, también presenta inconvenientes. Por ejemplo, el acabado superficial en superficies complejas puede tener una rugosidad elevada. Además, el tiempo de fabricación es elevado, los materiales tienen propiedades mecánicas y térmicas limitadas que limitan el comportamiento ante esfuerzos y las tolerancias son mayores que en otros métodos de fabricación como los basados en arranque de material.
Impresión 3D
La impresión mediante impresoras 3D, se entiende como una de las grandes revoluciones industriales de los próximos años. Existen propuestas para democratizar la fabricación de unidades de distribución de bajo coste RepRap a las personas de todo el mundo a través de comunidades de usuarios desarrolladores que intercambian modelos 3D, conocimientos y experiencias para optimizar la fabricación de una impresora 3D autoreplicante.
La fabricación aditiva como necesidad
Tal y como explicaban en un artículo en la revista Interempresas desde la Universidad Pontifica Comillas y del Área de Ingeniería del Diseño de UNED, la Unión Europea ha decidido que la fabricación en general, y la aditiva en particular, sea una de las herramientas clave para abordar algunos de los desafíos europeos y sus objetivos posteriores, sobre todo para el crecimiento y la creación de valor agregado de alta calidad de puestos de trabajo. Esta decisión está generando programas de apoyo y promoción de la investigación e innovación para conseguir que la fabricación aditiva permita ofrecer nuevos productos de alto valor, así como servicios competitivos.

Sectores clientes
Uno de los sectores de gran potencial para estas técnicas es el sector médico y odontológico y un buen ejemplo es el desarrollo de ‘brackets’ invisibles, que vienen a sustituir los antiguos de metal, menos estéticos. Se trata de un producto estrechamente ligado al diseño CAD, desarrollado mediante un proceso que supone una automatización muy ligada a la producción neta del producto. El proceso de invisibilidad, además, es aplicable también a otros campos de la medicina como las prótesis auditivas, donde la fabricación tradicional está siendo desplazada por las tecnologías 3D, permitiendo personalizar el producto a la forma de cada usuario. También existen productos como plantillas plantares, implantes quirúrgicos e incluso la reconstrucción de hueso en casos de cáncer (de mandíbula) o accidentes de moto (reconstrucciones de cráneos), sustituyendo las piezas metálicas utilizadas hasta ahora.
Los términos empleados habitualmente alrededor de la fabricación aditiva han ido evolucionando de forma paralela al desarrollo de la tecnología:
- ‘Rapid Prototyping’. Es el primer término que se utilizó para describir la creación mediante capas de objetos 3D. Actualmente, las tecnologías existentes, permiten conseguir algo más que un ‘prototipo’.
- ‘Impresión en 3D’. Es el término más utilizado. Es frecuente emplear el término de “Impresión en 3D de bajo coste” cuando empleamos máquinas de impresión de alcance doméstico o semiprofesional.
- ‘Fabricación Aditiva’. Es el último término aplicado y se utiliza para describir la tecnología en general. Es muy habitual cuando se hace referencia a aplicaciones industriales de fabricación de componentes y con equipos profesionales e industriales de altas prestaciones.
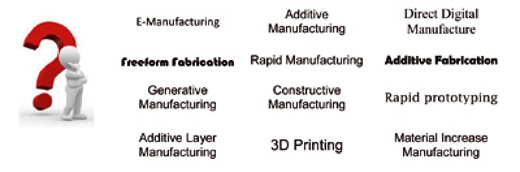
La diferencia entre estas técnicas se reduce a la aplicación que se le da a la tecnología de fabricación aditiva, es decir, la diferencia entre fabricar un objeto con una funcionalidad de comprobación ergonómica del diseño y fabricar un elemento que sirva de soporte para ajustar dos piezas en montaje, es nula cuando hablamos de su fabricación, el matiz reside en la función final que desempeñarán. De esta forma, se puede utilizar una técnica de prototipado rápido como posible tecnología de fabricación rápida de elementos, de herramientas o de moldes. El personal técnico, tiene que tener en cuenta que esta posibilidad deriva en una mayor simplicidad de los procesos de montaje y puesta a punto de elementos en su conjunto.
Una característica común a las diferentes técnicas de fabricación aditiva es la de requerir un mínimo número de fases en el proceso de fabricación, desde el desarrollo de la ‘idea’ por parte del diseñador hasta la obtención del producto acabado. Es el propio diseñador quien puede encargarse de la fabricación del producto. No es necesaria la intervención de otro técnico para realizar operaciones complementarias. No obstante, hay que tener en cuenta que durante el proceso y antes de la fabricación, el diseñador debe saber los condicionantes del producto final, tanto para saber elegir la técnica idónea de fabricación, como para realizar las modificaciones del fichero de datos geométrico (stl) y revisar el código CN.
Ventajas de la fabricación aditiva
Los procesos de fabricación de piezas convencionales están condicionados por una serie de limitaciones relacionadas con la obtención de ciertas formas, como agujeros con trayectoria curva, ángulos de desmoldeo, control de las colisiones de la herramienta con piezas de geometría compleja, sin olvidar que algunos procesos de fabricación no cumplen con un compromiso con la sostenibilidad en la fabricación y llevan asociados residuos relacionados con la utilización de los líquidos refrigerantes.
Las técnicas de fabricación aditiva se distinguen principalmente de las técnicas convencionales por dos características que, además, les confieren grandes ventajas competitivas en tanto en cuanto no encarecen el proceso de fabricación: la complejidad geométrica de la pieza a fabricar y la personalización del diseño de la pieza a fabricar.
- La complejidad geométrica de la pieza a fabricar: Se pueden reproducir fácilmente geometrías esbeltas, vaciados interiores, canales internos, espesores variables, formas irregulares, etc., y a partir de una geometría obtenida por un CAD 3D.
- La personalización del diseño de la pieza a fabricar: Podemos obtener productos exactamente iguales o completamente distintos sin influir notablemente en el proceso y sin costes adicionales. Esta personalización es una de las principales tendencias actualmente en el desarrollo de productos de alto valor añadido, y su aplicación en masa es uno de los paradigmas que persigue la industria en países desarrollados y que se considera clave para su sostenibilidad.
Estas dos características se pueden convertir en grandes ventajas en distintos sectores industriales:
- Productos aligerados. Se pueden fabricar productos diseñados para una determinada función y con condiciones a medida, por ejemplo: aligerados por razones de peso, resistencia y/o costes. Algunas de las técnicas de fabricación aditiva pueden rellenar un modelo con diferentes grados de porosidad sobre un mismo material.
- Productos multimaterial. Es posible fabricar un producto aportando simultáneamente varios materiales en un mismo sólido; de este modo, la técnica supera una de las limitaciones actuales en la relación peso/resistencia mecánica, aportando funcionalidades nuevas o abaratando costes del producto.
- Productos ergonómicos. El diseño de los componentes puede alcanzar una mejor interacción con el usuario adaptándose a las particularidades antropométricas exactas de cada individuo (prótesis) sin afectar necesariamente a los costes de fabricación.
- Mecanismos integrados en una misma pieza. Es posible fabricar un mecanismo totalmente embebido en la pieza en la que debe trabajar, sin necesidad de montajes y ajustes posteriores, por ejemplo: simultáneamente un eje y su cojinete, un rodamiento, un muelle y su soporte, un tornillo sinfín y su corona.
Ventajas
Desde el punto de vista de la producción de componentes industriales hay que destacar como claras ventajas:
- Reducción del ‘time to market’ de nuevos diseños.
- Series cortas de producción.
- Reducción de errores de montaje y sus costes asociados.
- Reducción de costes de inversión en utillaje.
- Procesos híbridos: siempre es posible combinar distintos procesos de fabricación.
- Optimización en la utilización de material. La reducción de residuos de material es mínima. El material generado como residuo puede reciclarse fácilmente.
- Provoca una fabricación más sostenible. No se utilizan directamente productos químicos tóxicos en una cantidad apreciable.