Aproximación al alivio de tensiones mediante vibración (VSR)
1. Introducción 1.1. Definición de tensiones residuales
Las tensiones residuales de un material o componente son las tensiones que existen en él cuando no hay (y a veces cuando ni siquiera ha habido anteriormente) solicitaciones o cargas externas. Los procesos de conformado son las causas más comunes que provocan tensiones residuales. Virtualmente todos los procesos de conformado, soldadura, mecanizado, moldeado, tratamientos térmicos, etc. pueden ser introducidas también más tarde a lo largo de la vida de la estructura por procedimientos de instalación o montaje, por sobrecargas asentamiento del suelo o estructuras subterráneas, o por cargas muertas que puedan llegar a ser parte integrante de la estructura.
Pueden dividirse en dos grandes grupos: macro y microtensiones, pudiendo hallarse ambas presentes al mismo tiempo (Figura 1). Las macro tensiones, que a menudo se denominan tensiones Tipo I, varían dentro del material de la pieza a lo largo de una distancia mucho mayor que el tamaño de grano. Por el contrario, el origen de las microtensiones se debe buscar en diferencias en la microestructura del material. A su vez estas tensiones suelen ser divididas en dos grupos; Tipo II y Tipo III. Las tensiones residuales Tipo II varían en la escala de un grano mientras las de Tipo III corresponden a las tensiones surgiendo dentro de un grano como consecuencia de la presencia de las dislocaciones u otros defectos cristalinos. Estas micro tensiones a menudo tienen su origen en la presencia de diferentes fases o constituyentes en un material [1].
![Figura 1. Diferentes tipos de tensiones residuales [2] Figura 1. Diferentes tipos de tensiones residuales [2]](https://img.interempresas.net/fotos/791427.jpeg)
1.2 Tratamientos de las tensiones residuales
1) Mecánicos: shot peening, hammer peening, needle peening, ultrasonic peening
2) No mecánicos: térmicos y por vibraciones
![Figura 2. Métodos de alivio de tensiones [3] Figura 2. Métodos de alivio de tensiones [3]](https://img.interempresas.net/fotos/791428.jpeg)
El alivio de tensiones mediante tratamiento térmico se realiza calentando la pieza o unión soldada a una temperatura y a un periodo de tiempo determinado. Se recomienda un calentamiento gradual uniforme de toda la pieza, un tiempo de permanencia a temperatura determinada (que en el caso de los aceros es alrededor de 600 °C durante una hora por pulgada de espesor), seguido de un enfriamiento igualmente gradual y uniforme. Cuando el material es sometido a un calentamiento, se produce en él una disminución de su límite elástico; como las tensiones residuales de los cordones de soldadura (especialmente las longitudinales) pueden alcanzar valores muy cercanos a éste, el nivel de las tensiones residuales se reducirá al redistribuirse para mantener el equilibrio de fuerzas. También es posible que se presenten mecanismos de termofluencia que relajen las tensiones durante el tratamiento térmico; sin embargo, para alcanzar un efecto importante se requieren permanencias prolongadas que no siempre son posibles en la práctica.
Para el alivio de tensiones por tratamientos mecánicos tenemos el de preestirado y mediante vibraciones.
1.2.1 Alivio de tensiones mediante vibración (VSR)
La posibilidad de utilizar las vibraciones para aliviar las tensiones se descubrió alrededor de 1943, durante la Segunda Guerra Mundial, cuando unas construcciones soldadas que se transportaron desde el taller de soldadura al taller de máquinas por tren y camión presentaron una menor distorsión cuando se mecanizaron. A medida que la guerra avanzaba, los alemanes introdujeron el “transporte después de la soldadura” en componentes de precisión de gran tamaño. Los ingenieros no sabían por qué ocurría este fenómeno, pero pensaron que era a consecuencia de los movimientos en la pieza de trabajo y comenzaron a experimentar y desarrollar métodos para generar los movimientos de una manera más controlada. Los estadounidenses también descubrieron que a través de las vibraciones inducidas en el material, las construcciones ganaban en precisión.
El alivio de tensiones por vibración es un método relativamente simple que induce vibraciones armónicas o sub-armónicas con gran amplitud en el material. El equipo habitual consta de una fuente eléctrica con una unidad de control, un motor eléctrico que gira excéntrica ((inductor de la fuerza) y un acelerómetro (transductor) que registra el flujo de frecuencia a través de la pieza de trabajo (Figura 3).
![Figura 3. Esquema de un equipo de alivio de tensiones por vibración [4] Figura 3. Esquema de un equipo de alivio de tensiones por vibración [4]](https://img.interempresas.net/fotos/791429.jpeg)
Todos los metales tienen una frecuencia armónica. El metal vibrará a esta frecuencia cuando se expone a un impacto repentino de ejemplo al martillar sobre una viga. Después del golpe, el metal vibra hasta que toda la energía se disipa a través de la fricción interna. El alivio de tensiones por vibración afecta el material similar al golpe de martillo. La diferencia se encuentra dentro de la fuente de vibración; ya que utiliza un motor eléctrico que genera un suministro constante de vibraciones. Cuando una pieza de trabajo se hace vibrar, el calor se acumula y causa un incremento infinitesimal de la temperatura en el interior del material, induciendo la energía suficiente para que las dislocaciones se reposicionen y vuelvan a un nivel de tensiones menor. De esta manera las tensiones residuales se reducen en el material.
Las vibraciones se inducen en la pieza de trabajo de dos maneras. Si la pieza de trabajo es lo suficientemente grande, el vibrador se puede conectar directamente en ella. La pieza de trabajo tiene que estar aislada del suelo con almohadillas de caucho para impedir que las vibraciones se extiendan a los alrededores. Otra forma es unir el vibrador a una mesa donde este anclada una o más piezas de trabajo y también estará aislada por almohadillas de goma, permitiendo el alivio de las tensiones de manera simultánea.
Las piezas pequeñas tienen que estar siempre ancladas a una tabla o mesa de trabajo para garantizar que la frecuencia armónica no esté fuera del rango del vibrador. La frecuencia de las vibraciones depende del material, tamaño y forma de la pieza de trabajo. Por lo general, la frecuencia de vibración está en el intervalo de 0-100Hz. El tiempo para el tratamiento de vibración es a menudo menos de 30 minutos (Figura 4). Se sabe que la aplicación en la que han demostrado mayor efectividad es en el control dimensional de estructuras soldadas [5].
![Figura 4. Tiempo vs peso de la pieza para conocer el tiempo necesario a vibración [6] Figura 4. Tiempo vs peso de la pieza para conocer el tiempo necesario a vibración [6]](https://img.interempresas.net/fotos/791432.jpeg)
Actualmente hay dos tipos de métodos disponibles de alivio de tensiones por vibración
Durante el primer método se hace un vibrado y barrido lento la pieza de trabajo desde la frecuencia cero a la frecuencia máxima, por ejemplo 0-100 Hz durante 8 minutos. La respuesta es analizada y su frecuencia armónica registrada. Por lo general, se registran dos o tres de esas frecuencias. El vibrador se ajusta y se cambia la velocidad a una que sea igual a la primera frecuencia armónica. La vibración sigue un tiempo dado, por lo general 10 minutos. Después de esto la velocidad del vibrador se incrementa a una que es igual a la siguiente frecuencia armónica superior y el proceso se repite.
El otro método, llamado sub-resonante tiene el mismo procedimiento de iniciación donde se registran las frecuencias armónicas y, luego, la frecuencia de las vibraciones se mantiene ligeramente por debajo del armónico, generalmente por debajo de 4 Hz. Cuando disminuye y estabiliza la primera frecuencia significa que se ha relajado la pieza de trabajo desde las tensiones residuales. El tiempo para que esto ocurra es de aproximadamente 20-30 minutos, dependiendo del tamaño de la pieza de trabajo (figura 5).
![Figura 5. Procedimiento de operación del método de alivio de tensiones sub-resonante [7] Figura 5. Procedimiento de operación del método de alivio de tensiones sub-resonante [7]](https://img.interempresas.net/fotos/791434.jpeg)
2. Aplicaciones Dentro de las aplicaciones encontradas en la referencia bibliográfica [6] tenemos:

3. Ventajas frente a las alternativas tradicionales
A diferente de los métodos para alivio de tensiones por tratamiento térmico, este método presente las diferentes ventajas como:
- El equipo es compacto y portátil, de este modo, puede moverse a cualquier parte de la planta de producción o incluso a trasladarlo fácilmente a otras empresas.
- Los costes de inversión, funcionamiento y mantenimiento son bajos.
- El proceso dura entre 15 y 30 minutos por ubicación, según el peso y configuración del componente o estructura.
- Es fácil de usar y no requiere la necesidad de extensas instrucciones para el operario
- Se puede usar en una amplia gama de materiales.
- No tiene efectos negativos en el material.
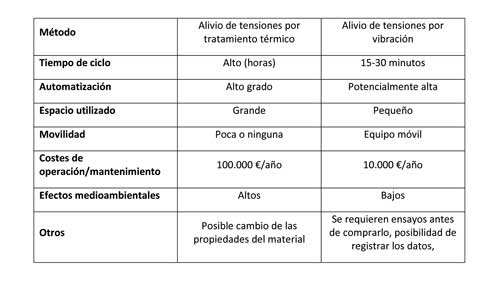
La tabla 1 hace una comparativa del alivio de tensiones por vibración con el método convencional.
Referencias
[1] A. M. Irisarri. Efecto de las tensiones residuales sobre las prestaciones de diversos componentes. Anales de Mecánica de la Fractura Vol. I, 2006, 245-250.
[2] P. J. Withers and H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia. Residual stress Part 1 – Measurement techniques. Materials Science and Technology, 2001, Vol. 17, 355-365.
[3] Tim Wessel. Stress Relieving Welds. US Army Corps of Engineers.
[4] http://www.gigabiz.co.uk/
[5] F. Casanova, D. Henao, F. Franco. Control dimensional de uniones soldadas utilizando tratamiento de alivio de tensiones mediante vibraciones. Revista Ingeniería e Investigación, Vol. 28, Nº 1, 2008, 22-25.
[6] http://www.metronicnet.com/pdf/Presentacion_estabilizador.pdf
[7] Stefan Lindqvist, Jonas Holmgren. Alternative Methods for Heat Stress Relief. Master of Science Programme, Mechanical Engineering Luleå University of Technology. Department of Applied Physics and Mechanical Engineering, 2007, 84 págs.















































































