Interview to Fernando Burguera, manager of the Area of Engineering Advanced of Batz

Fernando Burguera, manager of the Area of Engineering Advanced of Batz.
You have developed a pedalera manufactured in composite, what supposes a big evolution…
Like this is. The pedaleras have been present in the vehicles of engine from his origin, and always with a clear and clear-cut functionality. Although to be precise, this last is not of the all correct, since they exist determinate functions added that they can implement in the pedaleras.
For example?
Systems of hygiene to avoid damages to the inferior extremities of the users in case of collision, systems of adjustable pedals that displace and adapt to the ergonomics of the user, etc. Therefore, if the main function already is defined and is known and common to all the vehicles, what requires is an improvement in weight and cost to contribute to the improvement of the complete vehicle.
Of which way?
The steel with which do traditionally the pedals is reliable and known, but also very heavy and, according to which processes take part, expensive. The challenge of the design in plastic consists in achieving emulate the properties of rigidity and resistance of his homologous of steel, but keeping an important advantage in weight and cost. It is necessary to take into account that when we speak of pedaleras speak of the most critical piece of the vehicle, the one who never would want that it failed: the pedal of brake. The requirements for him, so much in rigidity as in resistance to the break, are brutal.
Logical…
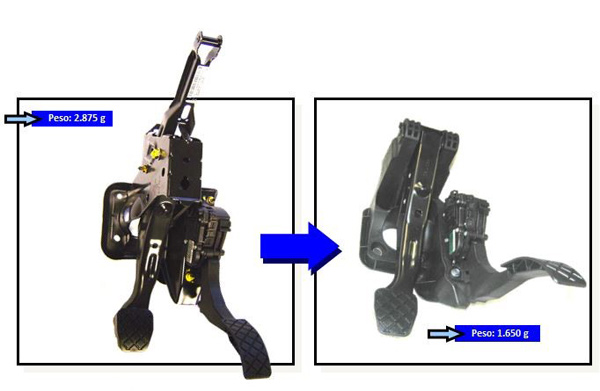
Traditionally the pedaleras manufacture with pieces of steel or metal stamped and joined or soldered between himself. If it substituted each piece individually by another piece of plastic, would follow needing a process of assembled and, with all hygiene, the competitiveness would reduce notably. However, the design of pieces of plastic allows a high degree of freedom of design and integration of pieces in an alone.
Really it contributes the same provision that the metal regarding resistance and hygiene?
There is an important factor to recalcar here, although it can seem obvious: the design in plastic of critical pieces mecánicamente never can be similar to the design realizar in steel or metal. The specific properties of the best of the plastics are far of what can obtain with steel, especially in rigidity.
Then?
It is necessary to pose the challenge to substitute as a whole a pedalera based in steel or metal by a based in plastic, no the replacement of each one of his components. Therefore, we can do the same current pieces of steel in plastic keeping the properties? No. We can, however, substitute a pedalera based in steel by another based in plastic keeping the properties? Yes, with a suitable design.
Also is necessary puntualizar that no all the pedalera goes to be of plastic, still there are redoubts that have to use metals, because of his high specific requests or because the particular geometry of a pedalera determined do not allow the necessary space for a design in plastic.
Which type of plastic is appropriate for this application?
When it speaks of utilisation of plastic in pedaleras it is necessary to take into account that the function is fundamentally structural, no aesthetic. We are not so mediatizados by the appearance that has to have the piece at the end, as by the fact that have a mechanical behaviour very high. The materials have to have loads of fibre that achieve to give him these properties. Usually they use polyamides and polipropilenos with percentages of fibre of glass that oscillate between 30% and 50%. Other matrices do not use so much. The fibres of carbon, vegetal, etc. neither have a significant presence. However, the plastic hybridisation-metal is a solution that can result highly competitive, as in which cases.
In which measure influences the material in the design of a pedalera? It differs a lot this according to the material employed?
In Batz try to work with basic materials the most economic possible to win in competitiveness. We prefer to use PP in place of PA if we achieve a design that fulfil with the requests, which is not easy. We are in automotive sector and the OEM never gives at all. A PP loaded with 30% of fibre of glass, for example, has a density 20% minor that his equivalent in PA. Since the price by kilo can be around 75% of the price of the PA, find us that a same design —and therefore a same volume— in PP+30GF is until 40% more economic that the same design in PA+30GF. Claro that the mechanical properties also are inferior, afterwards is necessary to analyse if it is feasible to develop the piece with this material optimised.
It can put an example?
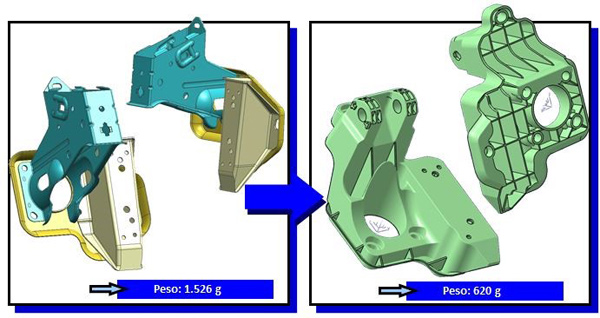
Yes, an example of optimisation in function of the material is the support of a pedalera, that can be a notably massive piece, inside the area in that we move us. The function of a support is, as his same name indicates, bear the rest of the components, especially the pedals, and the maximum loads to that are subjected. The most extreme case of abusive load produces on the brake, to guarantee that it never goes to fail into use normal. Afterwards, the zone of greater tensions in the support is precisely the accommodation of the pedal of the brake. If the tensions produced in the support in this zone are excessive for a PP with fibre, for example, a first solution would consist in migrating the material of the support to PA, for example, but this involves to change the material no only in the zone of the pedal of brake, that is the one who is more loaded, but also in all the rest of the support, sobredimensionándolo and sobrepreciándolo excessively. Here it is where it is necessary to look for solutions more imaginative that simply this migration to the upper material: look for designs, hybridisations or even alternative processes to try keep the competitiveness without altering the basic material.
It is that the main challenge to the that have confronted to the hour to substitute the metal by the plastic in the pedaleras?
Probably, our main challenge does not have at all that see with technical questions, but with appearances more psychological. “I understand your technical arguments, but you of what would want to that it was the brake of your car, of plastic or steel?”. This question, that has posed us in some OEM, is perhaps the most complicated to combat.
I understand…
Besides, from periods inmemoriales, the vehicles carry pedals of steel and, in general, do not give problems. Certainly, do something lighter and more economic is interesting, but can generate an uncertainty, a feeling of inhygiene, of jump to the empty that carry to the OEM to pose if it is worth it the risk. On the other hand, the user last does not go to perceive the change, no goes him to sell in the advertising that the pedals are of plastic, because, in fact, could be until contraproducente for the image of the vehicle.
And regarding technical challenges?
To be sincere, when you begin to work with plastics to substitute steel or metal is when you darse of the easy that results to design with metals. It would say that the main point to take into account is the big influence that has the process in the characteristic finals of the pieces of plastic. Certainly, the steel laminado neither is totally isotrópico, for example, but the difference of obviar this anisotropy does not be used to to be important, whereas in the plastic subjected to critical tensions is vital, as well as control other resultant appearances of the production, like the lines of welding. Besides, factors like the aging or the relaxations of tensions, that in the steel do not contemplate , win a main importance.
Which appearances have to take into account to the hour to design the pedaleras?
The pedalera is located in a place of difficult access inside the vehicle, usually between the firewall, the column of steering, the HVAC (system of air conditioning) and other adjacent elements. Also it influences notably the location of the elements acted, like servofreno and hydraulics cylinder of the embrague. Many of these elements have to can receive maintenance, what does that the available space for the pedalera was always committed. Besides, the additional functions that each OEM want to implement go to condition the design, like the system of hygiene in front of collisions, the fast unions to servofreno and cylinder of embrague, etc. With all this the first that has to realizar is to appreciate the available space and the admissible geometry for the pedals.
Geometry?
Yes, said geometry goes us to give an estimate of the usable materials. For example, the pedals of embrague and accelerator are used to to do in PA of usual form, but in some cases of forms especially narrow or twisted, the only solution is to go back to the metal. Later, there is an iteration of design-optimisation, that in the case of Batz, supports ventajosamente in the use of tools contrasted of topological optimisation.
With what objective?
Reduce weight and therefore cost of prime matter, but is the engineer of product together with the one of processes the one who has to study the usable options in each case and guide the iterations of design. There are more details that have to see with the parameters referents to the feelings perceived by the user, systems of assistance, ratios of transmission, etc., but that is another history that does not have so much that see with the materials in general.
The sector loans special attention to the reduction of the weight of the vehicles. What other parts traditionally feudos of the metal will be able to substitute in a future by plastic?
Batz Has developed a culture of aligeramiento concentrated in his current products. This culture does that we are investigating continuously in alternative materials (composites, magnesium, etc.), new processes (WIT, etc.) and, lately, in new products in which apply all these technologies developed. In the unit of business Batz Lightweight Technologies produce at present frontends and aerodynamic deflectors totally of plastic, in another sample of piece traditionally metallic migrated to plastic materials. This same movement can apply to other groups, so much to levels of mechanisms as of structural pieces, and appreciates that the irruption of the electrical vehicles with his need of aligeramiento to improve the autonomy and to compensate the weight of the batteries is pushing in this sense. But it is necessary to take into account that to achieve go in in a new function of the vehicle the saving of weight and cost is so only one of the factors to take into account.
In which projects works Batz in the actuality?
In technologies that allow us achieve pieces more economic even using processes more complicated. Specifically, we are investigating plastic pieces with technology WIT (Water Injection Technology) to allow a distribution of the most resistant material and rigid to equality of weight, or lighter to equality of resistance. Also it is working in hybrid pieces metal-plastic, with the optimum relation between both materials to achieve the ratio perfect resistance/rigidity and weigh/price. Another area of work are material alternative, so much in when to biopolymers based in PLA with natural fibres, as regarding textile of continuous fibre. Likewise, the expansion of all this knowledge generated to the rest of the current products of Batz, and to new developing products like active headrests, systems of elevation of spare wheel, crowbars of changes, etc.
The bet of Batz
Batz, S. Coop. It is a cooperative placed in the Group Mondragón, whose headquarters find in Igorre (Biscay). The company began his career 50 years ago producing coin of tooling. In the year 1982 created a new unit of business designated Systems of Automotive sector, devoted to produce components for vehicles, mostly metallic because of his previous culture. “It is in this unit where engloba the area of groups of pedals. An evolution accelerated in the last ten years has carried us to globalizar the activity, nowadays have a total of 14 productive plants around the world, and even diversify to other markets, like Power, but also to deepen in the challenges that poses us the evolution of our traditional products”, explains Burguera. The company works mainly in automotive sector, and this involves forzosamente a permanent investigation to the reduction of weight and cost. And here it is where the composites have an evident way to visit. “Our bet is firm until the point that recently it has created Batz Lightweight Technologies absorbing and improving another activity that was created already in 1992, devoted to structural and aerodynamic pieces in compound materials. All this diversification of activities does that we have to speak at present of the Group Batz, in which we work at present in the order of the 1.500 people”, aims.