Safety and hygiene in the plastic packaging industry
Pedro Melgarejo, technical specialist and Sergio Giménez, responsible for packaging and packing of Aimplas line
04/03/2010March 4, 2010
The regulation is understood as 'good manufacturing practice': "every aspect of quality assurance which guarantees that the materials and articles are produced and controlled in a consistent manner, to ensure that you conform to standards and the quality standards appropriate for the intended use and do not endanger human health or cause a" "unacceptable change in the composition of the foodstuffs or a deterioration in its organoleptic characteristics".
What companies does it affect the rules of procedure?
The scope of the regulation covers the companies that manufacture, process or distribute material that will be in contact with foodstuffs, including all possible sectors: plastics, materials and active and intelligent objects, glass, metals and alloyspaper and cardboard, ceramics, Cork, rubber, silicones, adhesives, printing inks, ion-exchange resins, regenerated cellulose, textile products, varnishes and coatings, waxes and wood, provided that all these will be for some period of his life in contact with any food product.
This have to meet a company for the implementation of Regulation (EC) 2023 / 2006?
Mainly, the company should establish and implement a 'system of Control and quality assurance' effective and documented, and at the same time ensure compliance. As noted in the preceding paragraph are defined two qualities that must comply with such a system of control and quality assurance. One of them is that the regulation calls for the control and quality assurance system to be effective, so that companies ensure that materials and finished articles meet food safety standards.
Another of the qualities which must have such a system is to be documented, committing the company to retain documents and records that demonstrate the effectiveness of the same.

How to set and a company applies a system of control and quality assurance?
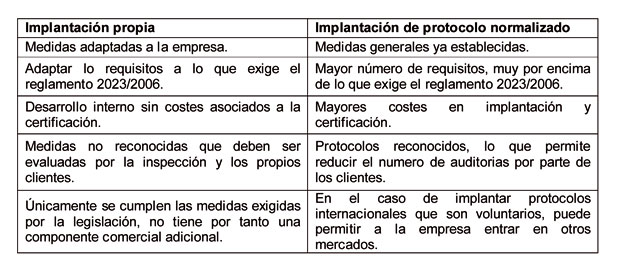
The regulation does not specify the methodology that should be carried out for compliance. For this reason, compliance will depend on the decision of the company and the strategy to decide to carry out enforcement. Currently there are two options: one is to establish a system of control and own quality assurance and the other option is to implement any of the standard protocols that exist already adapted to the food packaging industry.
From the experience of Aimplas, and after the audits carried out on various companies in the sector, can be said that the first option is the more expensive for the company as to establish the requirements to be met, but in turn has certain advantages. The main advantage that we find ourselves is that once implemented, it is usually a system better suited and less stringent than existing models.
The second option you can choose a company is to implement one of the protocols on the market, as it is the case of the BRC/IoP Protocol (British Retail Consortium / Institute of Packaging), the norm UNE - EN ISO 22000: 2005 or the norm UNE-EN 15593. The main advantage of the introduction of one of these protocols are defined points to meet, so it is easier the introduction and subsequent audit. They are also recognized by the sector, protocols which can be associated a reduction in the number of audits by the customers. However, its implementation takes partners certain external costs as well as being very demanding measures covering very than what requires the regulation 2023 / 2006.
What should you include a system of control and quality assurance to be effective?
A system of control and quality assurance must contain several aspects to be effective. The fields on which marking requirements to maintain an appropriate quality system are several.
As first premise, the system must identify and document all processes that are involved with the quality and hygiene of the final product. In addition, the system must have the implementation of a HACCP (hazard analysis and critical Control points) as one of the fundamental pillars. A HACCP helps the company to systematically identify all hazards that may affect the safety and future food hygiene which will come into contact with the materials, establishing and implementing mechanisms to control which do not exceed the critical limitsassociated with each of the critical points established throughout the whole process of production and distribution of food packaging.
Another section that has to contemplate a system of control and quality assurance is the requirements to ensure that the facilities of the company are kept with a level of hygiene to ensure the quality of the final product.
Finally, a good system of control and quality assurance should be seen in its structure a number of requirements regarding the staff, which define the awareness and training to ensure that the personnel involved in the processes of manufacture and distribution of products is aware of the importance of hygiene in the food chain.
What kind of critical points we are in the plastics industry?
The common critical point in plastic materials in contact with food, is undoubtedly, the overall and specific migration control. The plastic containers by their characteristics can suffer processes of interaction, both with food and with the environment around them. One of these processes is migration. Migration is the process by which substances contained in the plastic can be passed to the food that contain. Control of global migration, is focused on verifying the inertia of material and the specific migration control to rule out the problems of toxicity associated with a specific substance. Plastic materials depending on the food to contain and of the conditions of use, time and temperature of contact, should be evaluated according to their migration.
However, there are also other specific critical control points depending on the industry. One of them, which is also reflected in annex I to Regulation (EC) 2023 / 2006, is what affects the use of the materials printing inks. According to this annex business users must check that the inks are not in direct contact with food, as well as ensuring that they are completely dry so that there are free components that can happen to the food.
Another case is that occurs in the manufacturers of PET bottles for packaging food. A first step to obtaining the bottle, is obtaining from her preform pet. Her preform is a semimanufactured product that is obtained by injection and that is prior to the blowing end of the bottle. In this process of injection PET can produce acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde is a substance authorised in plastic materials in contact with food with a specific migration of 6 ppm limit, however, below this limit this substance can produce organoleptic taste and odor problems in the food, so their control is of vital importance.
On the other hand, in obtaining structures multi-layer plastic film, usual the use of adhesives based on polyurethane to unite different layers of plastic, these adhesives can produce a primary aromatic amines (AAPs) as a result of the reaction of one of the components of the adhesive, in particular the isocyanate, with water. The AAPs are regulated under the existing legislation with a limit of total content of 10 ppb. The AAPs are substances which will disappear over time, it is necessary that at the time of the packaging are already below the limit, but it is possible that they migrate to the product they contain. In this case, a control of these substances is required to avoid this problem.
As a summary, companies must have control mechanisms in the critical points of your process. These mechanisms shall be individuals from the production process of each company.