Progress of results of project Mepess
With this project Aimme is investigating how to produce with less weight, less material, less time to manufacture and cheaper pieces without giving up mechanical benefits. The sectors that directly affect the results of the project are the goods sector equipment, automotive, aeronautical, filters and heat exchangers and Biomedicine.
The project is still underway, so the results exposed here are those obtained so far.
Space structures
1. Framework of the project
During the years 2008 and 2009 Aimme product engineering unit is developing the project "spatial structures." in rapid manufacturing co-funded by the European Fund of regional development (ERDF) The main objective of the project is the study, analysis and manufacturing metallic parts aligeradas through a combination of two techniques: the design of selective spatial structures and additive manufacturing technologies. To ensure the prelas parts manufactured in this way. means rapid manufacturing or additive manufacturing technologies of construction directly parts by addition of material from electronic information. Geometric freedom that provides this new way of manufacturing allows arise new limits in the design of the products in two ways:
- Pieces with a structural zone, which gives the piece of special properties, such as greater elasticity.
- Looser pieces, which are composed of a solid area on the outside and a structural zone in the inland of the piece. the advantages of this new mode of design and manufacture of pieces are:
- Reduction of weight.
- Material savings.
- Improvement of the performance of the piece without increasing the weight.
- More awareness designs with the environment by reducing material and therefore less energy expenditure without compromising the quality and safety of products.
- New possibilities for design.
- Greater flexibility.
- Absorption of impacts.
- Thermal insulation.
- Reduction of costs.
- Reduction of the "time to market".
All these advantages are summarized in a single, "increase of the added value of a product and therefore increase in the competitiveness of the company have a differentiating element in light of the competition".
2. Results and applications
In general, structures can be applied to any piece of any sector wishing to incorporate the advantages described above. But in the sectors in which has been identified that there is a difference are:
- Capital equipment. Because of the flexibility and the easing of the pieces always fulfilling the intended function.
- Automotive. Given the importance of reduce the weight of the pieces without the necessary mechanical performance.
- Aeronautics. Given the importance of reduce the weight of the pieces without the necessary mechanical performance.
- Filters and heat exchangers. Introducing a structure increases the contact surface and therefore increases the efficiency of the same.
- Biomedicine: is currently under investigation in generating implants in metallic materials such as Titanium with use of structures to reduce the weight of the implant at the same time promote and enable the growth of the bone in the regeneration.
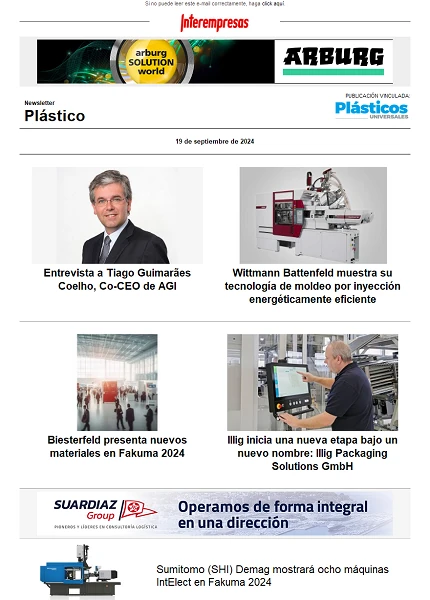
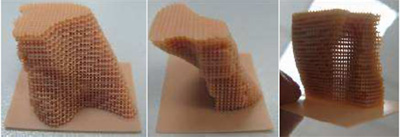
During the first months of the project, the efforts focused on the expansion of knowledge on space structures by analyzing solutions to structural problems. Different structures are designed and they are manufactured (Figure 1) in order to know the limits and characteristics of Rapid Manufacturing technologies, in particular Laser Cusing technologies for the fabrication of structures in steel, Fotopolimericación technologies for screening by mask (DLP)Stereolithography (SLA) for resins and fusion of metal dust by Jet of electrons EBM for titanium.
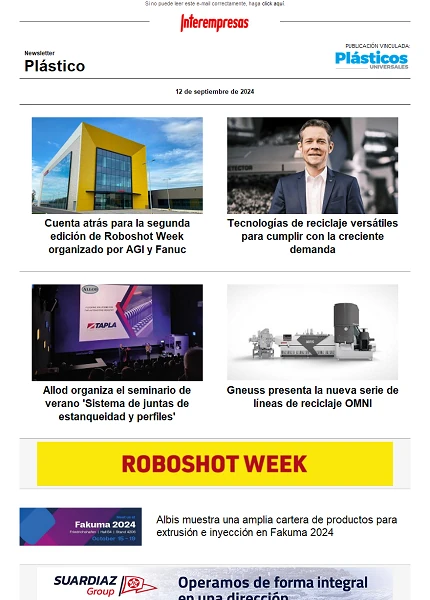
Today were are defining design criteria to help the designer to know the behavior of a piece that has internal structure structure. Traction and compression tests were being made to characterize the structures (Figure 2, Figure 3).

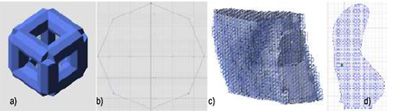
A specific software Netfabb Space Structures for the design of parts with structures that allow a fast and efficient adaptation of structures to volumes has been gained during the development of the project. Using this software, it is possible to generate different structures within a same solid as well as obtain a structure adapted to a certain form of surface (Figure 4).

As an example of application of the acquired software, is one of the provers that have been made in the course of the project, a piece of jaw which has filled up with a structure.
This demonstrator is manufactured with DLP technology and material E-Shell 200 South is certified with CE marking and is biocompatible with class II according to the ISO 10993 medical products act.
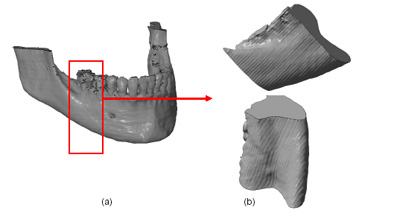
Figure 6 shows that the way each of the cells that form the structure and the way in which that structure adapts to the solid.
Below, in Figure 7 are images of the piece of jaw manufactured:
The project will continue its journey until the end of 2009, so that the exposed results correspond to activities definitive results.