The composite like material to mechanise
8 June 2012
Exist multiple types of compound materials that distinguish , mainly, by the origin of the matrix in which the aggregated incorporate (already was in shape of long fibre or particles of variable size distributed by the matrix). They exist three main types of compound materials:
- Material composed of ceramic matrix,
- material composed of metallic matrix, and
- material composed of polymeric matrix.
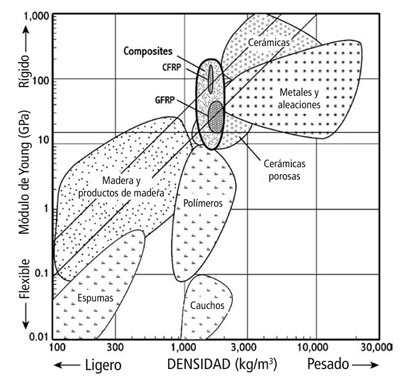
The compound materials (of polymeric matrix) present, therefore the following properties:
- Resistance to specific tension, between 4 and 6 greater times that the aluminium or the steel.
- The specific rigidity (the relation between the rigidity and the density) is between 3 and 5 upper times to the aluminium or to the steel.
- The compound materials provide important reductions of weight. This reduction depends of the type of solicitación and is so much elder what more uniaxiales are the efforts. In this case they can achieve reductions of weight between the 25 and 50% on the weight of the structure of aluminium.
- Excellent properties of amortiguación, thank you on the one hand to the discontinuidad of phases and by another to the behaviour viscoelástico of the polymeric matrix.
- Resistance to upper fatigue to the one of traditional metallic materials, approaching to 60% of the resistance to break (very upper to the one of the steel and the aluminium).
Need of mechanised
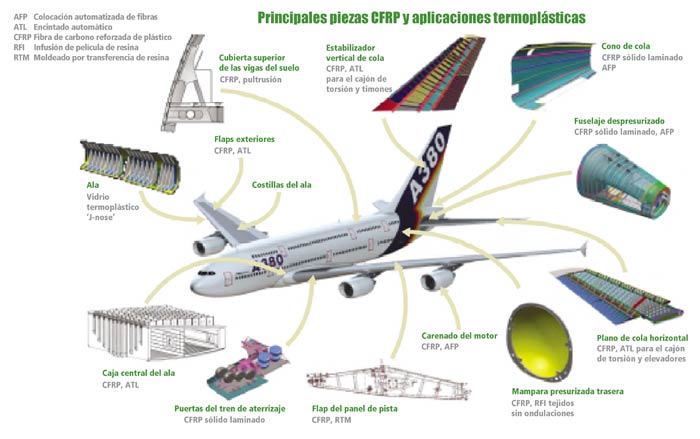
The processes of manufacture of compound materials do that his form was near to the real geometry wished (‘near-net shape') and therefore with needs to mechanise centred in two key technologies:
Endow to the piece of the final geometry, deleting the excess material that has deposited in the manual processes of deposition of fibre or cloths or the automatic processes as they can be the ATL or the AFP. For this uses the recanteado, that cuts the excess material geometrically. In function of the resultant superficial finishing, and the needs of the piece can add a process of rebabado.
The components of compound materials require his union to the rest of components of the structure, already are metals or compound materials. Taking into account that the welding is still in a state incipiente and the adhesive is complex (and prevents the desmontaje) the mechanical union of components by means of the remachado is, with difference, the most used technology. For this is necessary the taladrado of the structures for the placing of the vástagos of fixation. The specifications are usually diameter, position and geometry, as well as superficial quality obtained.
Precisely because of his structure and composition, the mechanised of the polymers reinforced with fibres of carbon differs to a large extent of the mechanised conventional of metals. They stand out, of this form, the presence of fibre highly abrasive that gives place to a remarkable wear of the tools, and to a resin, in general soft, and that limits the maximum temperature that it can generate during the mechanised. By a part, the resin is cut, whereas the fibre can be cut or fracturada. The orientation of the fibre, besides, gives place to distinct behaviours and, therefore, distinct finishings.
The main problems associated to the mechanised of the compound materials are the delaminación, the astillamiento or the thermal sensors damage:
- The structure laminar of the pieces of compound materials does that his properties of adhesion between the mentioned layers are minors that in the steering of the fibres. Of this form, a problem to avoid during the taladrado of the same is the delaminación, in which the strengths of cut in the steering of advance of the tool surpass the existent strengths between layers. In the taladrado, said delaminación produces mainly in the entrance or to the exit of the tool.
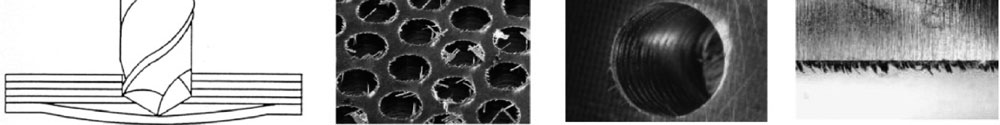
- thermal sensors sensors damage: the thermal sensors properties of the materials reinforced do that the heat generated during the process was absorbed mainly in the tool of cutting (50%), whereas in mechanised of metals, 75% of the heat is evacuated in the shavings. This generates two distinct problems: by a part, the temperature of work carries to an increase of the wear of the tool, and on the other hand, can generate thermal sensors damage in the resin that is mechanising .
- Another possible defect generated during the mechanised is the astillamiento. The mechanism of fracture of the fibre of carbon can give to place to that the cut of the fibre was not complete.
Finally, is necessary to mention that the high diversity of existent fibres, as well as of resins, and the presence of fibres in distinct orientations with regard to the piece comports necessarily an important variety of technicians of mechanised, as well as material and geometries of tools, according to the properties of resin and fibre.
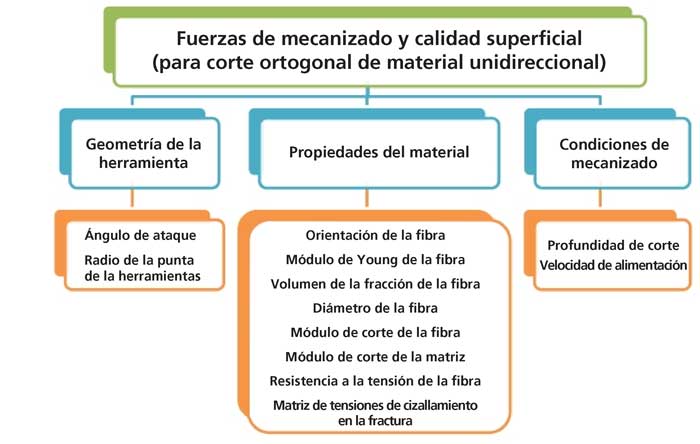
To solve this problematic, is necessary an integral approximation to the process of cut of materials composed in which they analyse the following factors:
Tools of cutting:
It Is necessary to distinguish in this appearance two components differentiated: the material of the tools of cut, and his geometry.
From the point of view of material, the traditionally employed tools for the taladrado of aluminium and CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced plastics) have been broaches of hard metal, the fast steel is not able to bear the abrasive character of the fibre of carbon. The possibility of recubrir the hard metal with coatings that protect the edge like AlTiN or diamond can serve to increase the life of the tool, but does not seem to improve the quality of the orifices realised neither the efforts of cutting. The broaches with teeth of PCD, already are ‘veined' inserted or simply soldered, does not improve the results.
Regarding his geometry, the main parameters that influence in the cut of composites are the angle of inclination, the radius of the tip of the tool and the angle of the propeller. The angle of inclination is the angle between the edge and the cut. To general way, positive angles allows to reduce the strengths of cut, whereas negative angles allow to generate one coins in the piece.
On the other hand, for compound materials, are preferable the tools with radio very small, being objective that his radius was minor that the diameter of the fibres (his diameter oscillates between 5 and 20 µm). However, an excessively small radius can weaken the cut and produce the plastification of the tool of cutting.
Another division of the tools is according to the existent propeller. The presence of a propeller generates a greater axial strength. Of this form, promote the delaminación. To avoid it, the manufacturers of tools are entering solutions based in a double propeller, that oponen mutually and generate compressesion of the material, hampering of this form the delaminación. Another alternative for this is to use teeth raunurados, that modify locally the angle of the propeller and avoid, also the delaminación.
For operations of taladrado, on the other hand, the geometry of the tip is of high importance to mechanise the materials composed in the suitable conditions. They stand out in this appearance, the conventional helicoidal tools, the ones of straight tooth, and the straight staggered tools or chaflanadas.
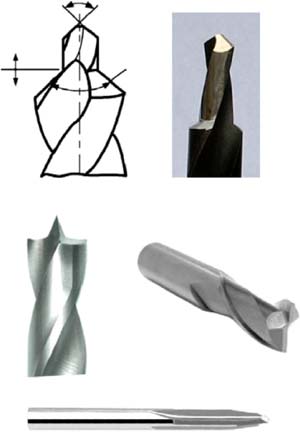
Strategy of cutting:
Two main parameters mark the superficial quality as well as the generation of delaminación in the zone of cutting: the speed of cutting and the advance.
Of this form, an increase in the speed of cut comports a reduction of the strength exerted and the torque, because of the warming of the tool and the material mechanised, although it is necessary to take into account that temperatures too high prejudice the quality of the resultant material. High values of advance generate similar damages to the produced by impact (delaminación staggered, cracks intralaminares…). With intermediate values of advance, the failures produce especially in the moments of entrance and exit of the tool. In particular, the notable factor for the taladrado of compound materials is the relation between the speed of cutting and the advance. For high relations, the surface obtained is soft and regulate, with minimum delaminación. For small values of this relation, exist significant damages, with delaminación that affects to distinct layers, and can produce desunión between the fibres.
Regarding his influence in the rugosidad, exist two distinct tendencies according to the percentage of fibre and resin. In compounds of fibre of glass with epoxy, the quality of the surface improves with the speed of cutting and the fraction of fibre. By the contrary, composites with a big percentage of fibre, comport of contrary form, being better high speeds of cutting and advances.
This remarkable influence of the parameters of work in the starts and finals of the holes does usual the modification of the parameters of work according to his height in the piece. This effect is still more stressed in the sandwiches metal-composite, in which they alternate layers of metal and of compound material, and metal, with high resistance to the impact, behaviour to fatigue. In these materials, is usual to use strategies to go in until a determinate point, for afterwards retreat and go back go in. So much in the materials laminados, as in compound materials, is usual to use speeds of exit slower to reduce the delaminación to the exit of the hole.
Incidentally to the already detailed problems of resultant quality, the resultant characteristics of the particles generated during the mechanised, that can give to place to problems of health of the operarios, as well as limit the flexibility of the system because of the presence of particles in the surroundings of work. To weigh that in the actuality the methods of external extraction equipment equipment are the most usual, are entering extractor systems equipment equipment of shaving through the tool with greater percentages of shaving absorbed.

Of this form, the compound materials require mainly recanteado and taladrado. In spite of the big differences with the conventional metals, the compound materials can be mechanised without defects from a control of the material and the geometry of the tool, as well as the strategy of cutting. Finally the problems of existent shaving in the compounds of fibre of carbon or of glass are solucionables from the extraction equipment equipment of shaving.















































































