Libertad in the design CAD thanks to the Additive Manufacture
Some of the technologies have reached a level of maturity such that allow to work with materials very known in the industry and, in the engineering, reaching the same mechanical characteristics that with other more known processes. And, what is more, that the increase of the complexity in the design do not increase to the cost of production but, as we will see in any of the following cases, even reduces it.
In this article refer us in scoop to products of metallic alloys obtained directly of machines of sinterizado laser.
The first of them refers a piece of big dimensions manufactured by injection of plastic, in the demanding sector of automotive sector, where the advantages of the additive technologies in collaboration with traditional technicians helped to solve problems of quality and dimensional.
In the second of them present how unify several pieces in an only block allows saving of costs in several fields in a small company, mainly in maintenance and stock of spare parts.
The third case speaks us of a piece of big destined complexity to the aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing sector, in which the additive manufacture no only saves costs but besides shortens a lot elo time of manufacture, from the design until the final piece list for his use.
Injection of plastic
The field of the moldeo by injection is one of which better and more spectacular results is obtaining with the application of the additive technologies. The main reason for this is that they allow to manufacture channels conformales of refrigeration very complex and perfectly optimised to the geometry of the piece, that of another way would be impossible to achieve with conventional technologies, in some terms of similar times and with some budgets of the same order; in general, they would be directly impossible to achieve.
The case in question is a piece of big dimensions and high value /750 cm3), with tolerances very narrow, high dimensional and aesthetic requirements, with zones of walls very fine between big masses of material connected by zones in passing very narrow.
When a mould does not cool of the correct form can produce in the piece defects of quality like looks, lines of different colour, zones without filling, fragile zones or retorcimientos and unacceptable deformations. For this there is a solution that consists in expecting more time with the piece inside the mould until all to the plastic have solidified , solution that puts up the price of tremendously the process.
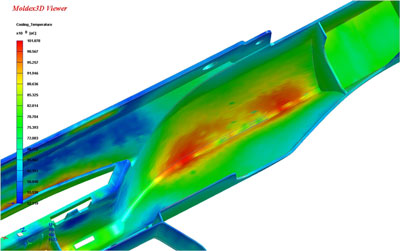
By means of a design optimised of the channels of refrigeration —creating channels conformales— achieves supply the suitable quantity of fluent refrigerante to the optimum distance of the piece in relation with the quantity of material to cool (thickness of material) and to the flow wished of heat (speed of cooling in each point). With this improves a lot the performance of the process because they can achieve decreases very important of the time of cycle from among 20% and 60% (abaratar the cost by piece) at the same time that it improves a lot the quality of the final product, in aesthetics, mechanical and dimensional characteristics.
In this case have had the narrow collaboration of a skilled company in the design of moulds of injection and in the simulation of the process that with the help of specific software can simulate the effect that on the process of injection has the geometry of the channels of refrigeration.
The design of the existent mould before our intervention —with the traditional technology of straight channels to base of taladros and caps— leaves some zones with a too high temperature at the end of the 56 seconds that lasted the cycle of injection. The distribution of density of material is not adapted and the gradient of temperatures between some zones and others also is too high. This does that the pieces twist (geometrical defect) when finishing to cool out of the mould and present superficial defects.
The solution adopted consists in building an insert with an efficiency of refrigeration adapted to the needs of each one of the three problematic zones. In the figure 3 shows the external surface of one of the insertos and the traditional system of cooling. In the inferior part shows the geometry of the channel conformed obtained after several iteraciones of the process of design and simulation.
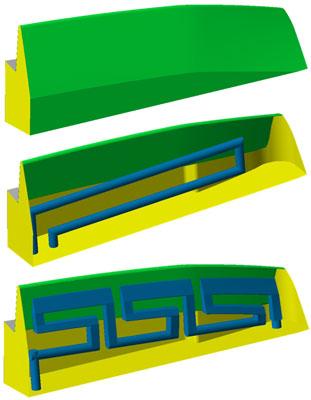
Is quite obvious that these geometries espirales, and curves with change of section can not manufacture unless the precision and material allow us attend to processes of smelting to the stray wax, what is not applicable for the moulds of injection of big series. However, the technologies of manufacture by addition of layers (AM) allow to manufacture these complex geometries until limits never seen up to now.
In his against has to indicate that they result very ineficientes to manufacture simple and massive forms, for what the technologies of start of shaving are perfectly adapted and optimised.
In this case big part of the success has been due to the suitable combination of both to obtain a product —the insertos— very effective and to a very competitive price.

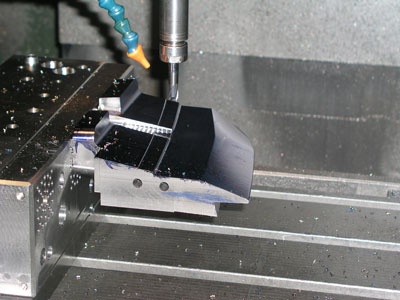
Although the three insertos have distinct geometry manufactured simultaneously in an alone platform of a machine EOSINT M270 using material 1.2738 TS. Once manufactured proceeds to the mechanised and finishing by traditional systems of mechanised and polishing.
The results obtained for the injection of the piece correspond with the obtained in the simulation by finite elements (UGLY) of the process of injection. It has been able to reduce the time of injection from the 56 initial seconds until so only 35 (reduction of 37%) at the same time that improves the density of the material and the half temperature diminishes. In the moment of the eyección of the piece no longer there is any point above the temperature of solidification but some 20 °C further down, what reduces virtually to zero the retorcimiento and improvement notably the visual quality.
The rhythm of production has happened of a piece by minute with defects of quality to almost two good pieces by minute, with an increase of the cost of the insertos of little more than 20% including so much the engineering and simulation like the manufacture by additive technology.
Reduccion Of maintenances
Bionorte Is an Asturian company that produces biodiésel and other by-products of high value added from residual vegetal oils. In a concrete point of the installation exists a bomb for the fluids of process, whose state has big influence in the productivity of the plant and in the quality of the final product. Like this it is that in what it begins to deteriorate the rodete has to be replaced immediately to avoid the costs of no quality and of low efficiency of the plant. Although the stop for the change of the element is not very long, the length of the same comes to be of some two months, with a cost of pieces of reasonable spare, pertinent of a foreign manufacturer with long term of delivery between 5 and 8 weeks. This forces to the company to have stock of piece of spare.

In this case has proceeded to the design of a substitutive piece of the three that conform the rodete, so that they can manufacture integrated cheese cheese in an alone by means of additive manufacture directly in stainless steel, in a system EOSINT M-270. The cost of the reingeniería has been of roughly the half of the cost of the group of spare and the manufacture of the piece directly in metal, including the costs of mechanised and finishing of the zones of seat, etc. has been a bit more than the double that the spare group original.

The new piece was put in operation in July of 2011 and carries working since to full performance and without apparent deterioration. This has to definitely to the robustness of the new design in an alone piece. Apparently it supposes an important extra cost concerning the original spare. Nevertheless, since up to now they have avoided already six changes, the company has saved already 4 times the cost in pieces of spare, the hand of work, the cost of the time of stop, the costs of no quality and rejections or reprocesos, although it is true that has had to invest a small quantity in engineering in the engineering of the piece.

Instrumentacion aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing
Ramem Is a Madrilenian SME of familiar origin, founded in 1958, devoted since to the design and manufacture of mechanical and electromechanical equipment for the industry in general, that has gone evolving from the manufacture of toolings for the sector of the automotive sector in his starts, to the aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing sector in the years 70, and to the aerospace and scientific activity, so much civil like being a member of the actuality (Eurofigther, Airbus To380, International Space Station, Big Telescope of Canaries, ESRF, ALBA).
The case that presents us is the one of manufacture of some Rake of instrumentation of pressesure to measure the profiles of speed of gases to the exit of the turbines of reaction, generally of aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing use. The main request of these pieces is that they can work to high temperatures (until 900 °C) resisting to the environingingment corrosivo that suppose the gases of leakage, without merma in his mechanical resistance by fluencia (creep).
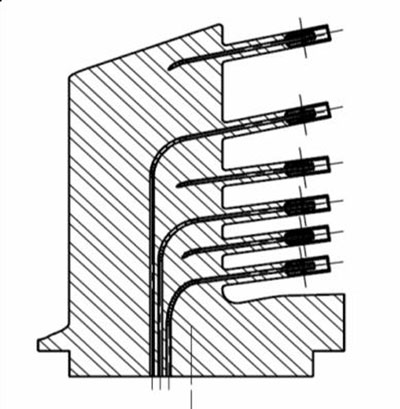
At the same time and given the dimensions requires a big precision: each one of the tubitos aims in a determinate steering and in his interior lodge a structure of protection and a channel of some 0,5 mm of diameter that arrives until the base of the element. All the channels are independent between himself and can not communicate.
The material of manufacture is the alloy IN 718, material widely used in the motors of aviation for gathering the mentioned characteristic. Nevertheless it is a material of processed complex since it toughens enormously in the processes of mechanised successive. The current process involves to split of a block of material to the that deletes by mechanised roughly 60% of the material to leave a preforma approximate to the final.
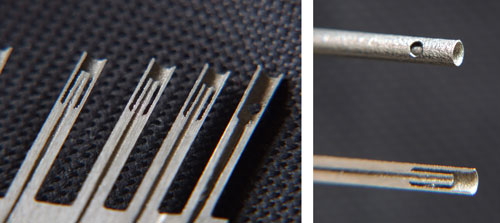
In this preforma cuts a channel with a high degree of precision and manufactures one covers for the same with suitable lace and that it can glide until his position. By means of spark-erosion leaves the form of each external tube of protection with his tubito inner.
Next manufacture separately each one of the tubitos and bend until the suitable position and sueldan by brazing to each one of the obtained in the preforma. The process is very laborious and delicate given the thinness of the walls and the diameters diminutos. All they place and adjust in position on the preforma, driving the tubes until one covers in the inferior part of the Rake. To continuation places covers it deslizante and suelda. It continues with the mechanised final and the final polishing.
The employment of the procedure of additive manufacture by means of sinterizado laser (DMLS) allows to build it of an alone time, in an only block, in the material elected Inconel 718, in a system EOSINT M280 in atmosphere of Argon. The precision of these systems allows to obtain the fine geometries without any problem in the orientation required. A step of spark-erosion allows to adjust the tolerances and the rugosidad, and a back polishing finishes the process.
The replacement by the process of additive manufacture supposes to reduce the term of manufacture from the 16 current weeks until so only four, increase the precision for deleting manual operations of bent and welding, reduce 60% of the cost and especially increase the robustness of the group when avoiding settings by parts, unions, etc.
has to consider besides that given the characteristics of these systems of additive manufacture can manufacture simultaneously several Rakes even different between yes, diminishing even more the cost and term of production.
















































































