Manufacture by addition of layers: the new industrial revolution
14 February 2012

The additive manufacture, or Additive Manufacturing as it knows internationally, consists in the successive superposición of layers micrométricas of material, usually in shape of dust until achieving the object wished. The consolidation of the material in each one of the layers achieves of distinct way according to the technology. This modality of manufacture supposes a new industrial revolution, intimately linked with the development of the TIC, and is the angular piece of the factory of the digital era and of the industrial future of the developed countries when allowing, between other advantages, prescindir of tools and toolings of manufacture, reproduce any geometry that the human being can imagine, offer an immediate answer to the cambiantes needs of the market and attend to the increasing demand of differentiation and personalización of the products by part of the consumers.
Of the industrial factory to the ‘Digital Factory 2.0'
In the three last decades has produced a transition to the digital in all the fields and the factories have not been extraneous to this phenomenon incorporating from systems of Aided by Design Computation (CAD), software of Aided by Manufacture Computer (CAM), going through the employment of automatons and robots, the inspection of quality by means of artificial vision and the control of the advance of the production in real time (MONTH), until the modelling and virtual recreation of processes and whole factories with software of simulation (CAPE).
All these advances have allowed to process to big speed ingentes quantities of data and handle mechanical systems, surpassing the limits known of reliability and precision but, however, the processes of manufacture, although aided by controls more advanced keep on being mayormente traditional by start of material, by smelting or by injection. These methods confront to limitations, no longer of control, but physical, like the impossibility to realise taladros curvos, the collisions of tools with the piece of complex geometry, or the restrictions of angles of desmoldeo, for example, that block the creativity and constitute a barrier, many times infranqueable, to the development of new products of high value added or with new functionalities.
As it collects in the document of Cotec, the technologies of additive manufacture, taking advantage of the knowledge of the digital era, allow to surpass these limitations and suppose an authentic revolution with regard to the traditional processes of manufacture when allowing manufacture by deposition controlled of material, layer to layer, contributing exclusively there where is necessary, until achieving the geometry wished, in place to start material (mechanised, coined, …), or conform with help of toolings and moulds (smelting, injection, folded, …).
Are very diverse the technicians of additive manufacture like the estereolitografía or the sinterizado selective laser, that allow to obtain pieces from an archive CAD 3D, ‘printing them' of form totally controlled on a surface. Therefore also they have employed other terms to refer to them as and-manufacturing (electronic manufacture), Direct Manufacturing (direct manufacture) or Additive Layer Manufacturing-ALM (additive manufacture by layers).
The main characteristic that distinguish the processes of additive manufacture of any another traditional process and that confer him big competitive advantages are:
- The geometrical complexity that has to achieve does not put up the price of the process. Characteristics like the esbeltez, an inner casting, internal channels, the variable thicknesses, the irregular forms and even the reproduction of the nature (pursuing ergonomics, aerodynamic, hydrodynamic, amongst other) are challenges that the conventional methods (sustractivos and conformativos) of manufacture have not resolved more than with approximations, assemblings or by means of processes of very high cost, and that for the additive manufacture are, in a lot of occasions, properties very little notable to the hour to manufacture a piece.
- With the additive manufacture, the personalización does not put up the price of the process because it allows to manufacture products, without penalising the cost, independently of if it has to manufacture a determinate number of equal pieces or all distinct, what facilitates the personalización, that is one of the main current tendencies in the development of products of high value added and one of the paradigms that pursues the industry in the developed countries when considering it key for his sustainability.
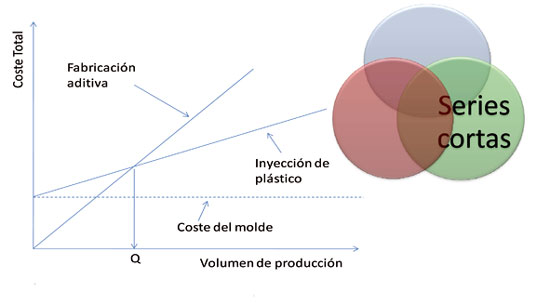
- Competitive manufacture of short series of products. Depending of the number of pieces to manufacture does necessary study from which quantity of pieces is profitable to manufacture traditionally, for example through mould of injection, or if by the contrary is more profitable to produce the pieces by additive manufacture, where adds the advantage to be able to realise modifications during the life of the product without hardly additional cost or parametrizar the product and manufacture it according to need, without being tied to a costly mould (initial cost, maintenance, storage, …).
These characteristics suppose a radical change in the process of design of the products and allow big creative freedom, as well as the exact reply of theoretical models of engineering without the approximations that impose the methods sustractivos or conformativos, so that it could affirm that with the additive manufacture can manufacture any object near at hand of the human imagination. Another advantage of the geometrical freedom that confer these technologies is the adaptation of the products to the biomecánica human, so that the designs reach a better interaction with the user and adapt no only to some standard sizes, but exactly to the peculiarities antropométricas of each individual, without affecting to the costs of manufacture.
Besides, these processes of manufacture allow to integrate distinct geometries and materials in a same object to achieve even that simultaneously it manufacture an axis and his cojinete, a rolling, a dock and his support, a screw and his crown, that is to say, a totally integrated cheese cheese mechanism in the piece in which it will have to work, without need of armed and adjust back. Also they allow to play with the porosidad of a same material or manufacture contributing simultaneously several materials in a same solid, surpassing like this the limitations that impose the processes of traditional in the relation weigh/mechanical resistance, contributing new functionalities and abaratando the costs of the materials.
Although they exist at present limitations and technological challenges that they have to be resolved, the enormous potential of the advantages that the technology contributes when changing conceptually the form to manufacture (of the sustractivo to the additive), opens an infinite world of interesantísimas opportunities of new products and models of business for the future. Knowing the evolution that have had other technologies in the past in little time, it will be necessary to ask until where will arrive this technology in the next years. To the equal that nowadays is normal to have of a printer of paper in our houses, will arrive to have of printers 3D in the houses of our children so that they manufacture his own products, that previously have designed?, which interrelationship will arise with the social networks, where a group colaborativo of professionals or final consumers can conceive, design and manufacture products locally under demand, personalised, …?, we find us in front of a new concept of manufacture, the digital factory 2.0? Nowadays, the additive manufacture allows already this.
Medicine, aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing, automotive sector, jewellery, art and textile, between his main applications
The sectors where the technologies of additive manufacture already employ at present are, amongst other, the automotive sector, the aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing, the jewellery, the art, the textile sector and the doctor, but also has a big potential in the industry manufacturera in general and in new economic sectors like the one of the video games.
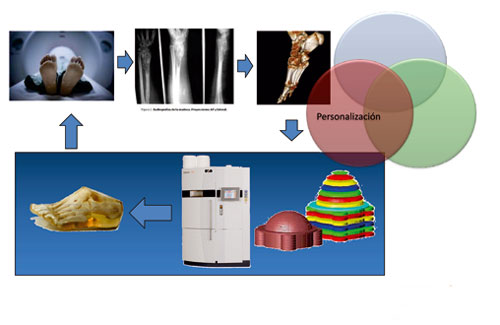
The medical sector has been an engine for the development of the technology from his origins and one of the main manufacturers of machinery for additive manufacture identifies this sector like the one of greater application of the products manufactured with this technology (23%), followed of the sector of automotive sector (15%) and the aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing (15%). This high interest has to , amongst other reasons, to the need of only pieces and of geometrical models of big complexity to adapt well to the human body, in addition to the familiarity between the systems of capture of medical data (TAC, scanner, …) and the technicians of treatment of necessary files for the additive manufacture, so that it is possible to integrate them with relative ease.
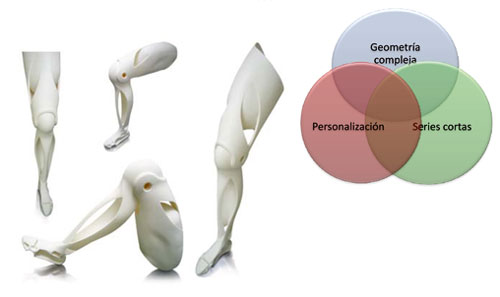
Between the susbsectores medical of application fits to stand out the biomodelos, to reproduce of exact way parts or the whole of the body of a patient, with the end that the surgeon can schedule a complex surgical intervention; the artificial implants customised of hearing, dental, articular prostheses to measure (knee, shoulder, hip, …); instrumental surgical and tools of help in the interventions; and the ‘scaffolds', that are porous structures that propician the growth of artificial fabrics, like the osseous or the cartilaginous, and that every time are more employed in engineering tisular. The additive manufacture allows, in this case, manufacture these structures with all the complication that require , achieving forms in 3D in which the new fabric can approximate perfectly to his final form.
The technologies of additive manufacture also attend the exigencias of the aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing sector, in which the low volumes of manufacture, the need of an optimum commitment between the mechanical resistance of the pieces and his weight, the personalización and the need to use complex geometries do them unbeatable in front of processes of traditional manufacture. And to the ones of the sector of automotive sector, in which the big constructors already are applying these technologies for the manufacture of prototypes and for the validation of the first series of the new models, and of the Formula 1, to give answer to the requirements of mechanical resistance with reduction of weight, exigencias aerodynamic and personalización of each escudería.
Other sectors of application are those intensive in design like the ones of jewellery, art, textile and furniture that take advantage of the advantages of the additive manufacture regarding the absolute freedom to design any form, by very complex that result, and to the rapidity in the rediseño; the sector of the mould and the matricería, to build moulds or parts of moulds of manufacture very complex, with characteristics like inner channels of refrigeration to control the refrigeration of the piece there where need ; or in the sector of the video games, when allowing the exact manufacture in three dimensions of the virtual characters or ‘avatars'.















































































