Tubular threads for union of voestalpine Böhler Welding
José María Miguel and Carlos Pérez of
Operation of the tubular thread
Exist two types of main process (autoprotegido and protected with gas) that give place to different mechanical properties. The case of the process autoprotegido account like main advantage the no utilisation of gas of external protection, but it is the same decomposition of the flux internal that guarantees the no gone in of air in the deposit of welding.
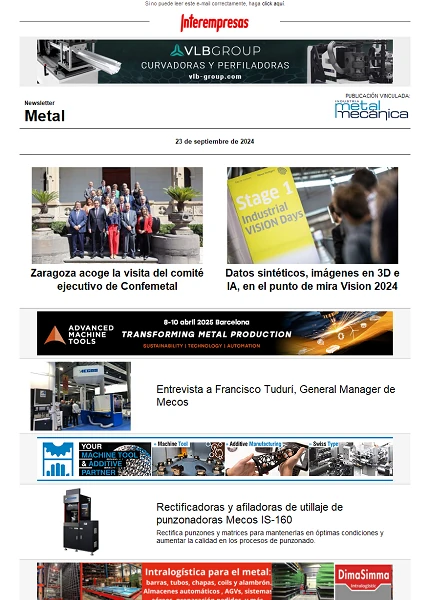
The Figure 1 sample the general process of welding with tubular thread, where by effect of a current between the piece to solder and the electrode, generates an electrical arch that gives place to the power calorífica necessary to produce the fusion of the metallic part of the tubular thread and the generation of gases and slag because of the ceramic components (flux) of the same. The slag solidified remains above the metal of welding, protecting it of the effect of the pollution or oxidation of the air. Likewise, the fast solidification of the flux facilitates the welding in vertical ascendant and low ceiling, positions of more difficult soldabilidad for the wire macizo.
There are several differences to quantitative level between the thread macizo and the tubular thread that have to consider to select one or another:
- Efficiency of the process: we will define this parameter like the percentage of weight of metal deposited divided between the weight of consumables used. The existence of projections and the learning of slag are factors that will do to diminish this factor. In case of the thread macizo the half efficiency is situated between 98-100%, tubular thread metal cored between 96-98%, tubular thread with fundente basic between 85-94% and finally tubular thread with fundente rutile 83-92%.
- Density of current: we will define this parameter like the intensity applied to melt the thread between the effective section (metallic) of the same. In the case of the tubular thread, when being hollow, has a lower effective section. In case to apply 270 Amperes, would obtain a density of current of 400 To/mm2 for the tubular thread, whereas only 240 To/mm2 for the wire macizo. This fact repercute in a greater speed of fusion for the tubular thread.
- Possibility to solder in different positions: The tubular thread with slag of rutile gives especially very good results in the welding of the most difficult positions, for example, under ceiling or vertical ascendant.
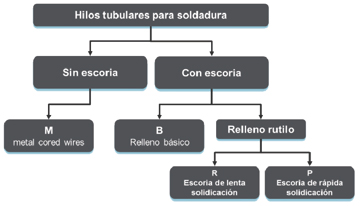
Types of tubular thread
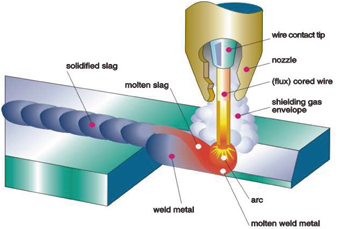
Exist two types of tubular threads according to his procedure of manufacture, giving place to consumables of behaviour in front of the soldabilidad different, as well as characteristic metallurgical and compositions slightly diverse. The Figure 2 pretends to show the two different routes of manufacture originating these two types of tubular threads (with and without sewing)
The tubular threads without sewing and cobreados realizar from a tube soldered by high frequency (are therefore totally tight). After several processes of inner cleaning and outside in this tube soldered realizar the introduction of the fundente (flux) by the top and mediane vibration this fundente goes delivering homogéneamente in the interior of the tube. Of this way, and in an alone stage, can realizar the filling of several cientos of kg of tube soldered. Later this tube trefila, reducing his thickness until obtaining the conventional diameters (for example, consumables for union of diameter 1.6 mm and 1.2 mm). The cobreado superficial realizar afterwards in a bathroom of suitable composition. Finally the material coil in the suitable format of supply (coils of 15kg, ecodrums 250kg, etc).
The tubular threads with sewing manufacture by means of a more conventional process in which it splits of a metallic band. After a partial deformation of the same, enters the fundente in his interior, and later, by means of a series of rollers of conformed, the band closes entirely. The tubular thread obtained is of a thickness that can not use directly, by what is necessary trefilar until the dimension of conventional utilisation, for example, 1.2 mm and 1.6 mm. Finally coil in the suitable format.
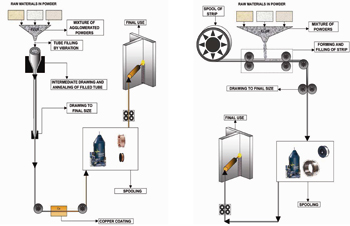
Like result of the two different routes of production manufacture two types of tubular threads, thread without sewing and cobreado and thread with sewing and without cobrear (Figure 3). To continuation expose his main characteristics:
Tubular thread without sewing and cobreado:
- Greater thickness of the metallic tube, what facilitates an optimum positioning for the welding automated. The greater rigidity of the thread does that it exist lower deviations in the arch during the process of welding.
- 100% cobreado by what exists a better transfer of the current and an upper resistance to the corrosion. Like this then , the surface of the wire will remain a greater time without deteriorating.
- Lower content of humidity in the interior of the thread put that it does not have sewing and, therefore, does not exist the possibility of entrance of the same in his interior. It does not do fault therefore resecado (rebacking) of the previous thread utilisation, by what is especially interesting in applications offshore and in conditions where the content of humidity is especially high.
Tubular thread with sewing and without cobrear:
- The proportion (in percentage) of flux that can contain these tubular threads is upper by what is easier to optimise his composition to facilitate the soldabilidad. Of equal form, also can contain a greater quantity of elements of alloy and like this is possible to realizar consumables of greater alloy.
- The fundente is 100% homogeneamente distributed in the interior of the thread since his constant filled facilitates that the composition of the fundente was equivalent in all the interior of the tubular thread. Like result will obtain an consumables with mechanical properties and of soldabilidad constant.
- The degree of deformation to the cual sees subjected the metallic tube is relatively low, which does feasible the production of threads of high alloy and basic qualities nickel.
- Treats of a process of production in continuous, by what is more stable and the most constant quality.
- Exists a variant in which in his last stage exists a sealed of the thread by means of a do laser. In this process, because of the contribution calorífico of a laser, melts partially the board (sewing), by what diminishes the entrance of humidity in the fundente internal causing of this way that the deposits contain lower quantity of hydrogen.
The Figure 4 presents of schematic form the diverse types of existent tubular threads in function of the components of the fundente. The mechanical properties and of soldabilidad that obtain are also different.
The tubular threads metal cored contain a filling almost totally entirely constituted by metallic dust with elements desoxidantes and almost any element formador of slag. It is of particular use to avoid the faults of fusion, in the obtaining of deposits without porosidad neither projections and when it requires a high speed of welding. The deposits are used to to work well after thermal sensors treatments, give especially good results when suelda in position 1G and 2G and can realizar the past of root without need of backrest.
The tubular threads with basic slag have like main characteristics the good properties of resistance to the fatigue, especially for thicknesses of wall elevated. His adecuación to the thermal sensors treatments is good and prefer use in flat position, with backrest if it realizar the past of root.
The tubular threads with slag rutile have like main application the welding in all position of material (are easy to manipulate) and have a very easy elimination of slag. The appearance of the cord is good and give place to few projections. However, only some of these threads are applicable when they exist thermal sensors treatments.
Applications of the tubular threads
The applications of the tubular threads are very diverse, depending to a large extent of the type of fundente and the alloy that deposits . Centring us in the consumables basic ironinging no aleados and of low alloy, the main applications and alloys are the following:
1) metallic Structure, nautics construction, wind mills and works of big envergadura (for example, bridges): The tubular threads are widely used because of his good speed of deposition and possibility to solder in vertical ascendant. The consumables type rutile (And71T1 —Böhler You46 FD—), basic (And70T5 —Böhler kb 52 T FD—) and metal cored (And70C6 —Böhler HL 51 FD—) adapt to solder the family of steels type S355 and S275. In some occasions and because of requirements of impact to low temperature (-50°C, case S355NL) has to employ an consumables that allow his utilisation in these conditions and even can demand that have the beneplacito of some companies of certification. To fulfil these severe requirements regarding the impacts requires an consumables with a low but controlled content of Nickel (And81T1 —Böhler You 60 T FD—), being required depending of the code employed, a back thermal sensors treatment to the welding (Figure 5). An important group of basic steels to consider are the resistant to the atmospheric corrosion (commercial marks Cut, Patinox), existing for them consumables compatible regarding his characteristics.

2) Components realizar in steel of high resistance: Cranes, equipment of heavy transport, machinery of minería, pipes of high pressesure (Figure 6). The most extended steels of this group would be the S690QL, S890QL, S960QL and S1100QL. The consumables used can reach, in the more extreme of the cases, a mechanical resistance slightly upper to 1000MPa and elastic limit above 900 MPa (And120T5 —Böhler Kb 90 T FD—). It is of extremada importance that the consumables employed contain the minor contained of possible humidity to avoid the agrietamiento by effect of the hydrogen. For example, in steels with an elastic limit of 700 MPa is necessary a content of hydrogen difusible in the metal of inferior welding to 5 ml/100 g. The tubular threads without sewing (that have contained of humidity very low) are the best candidates for this group of applications.

3) Equipment designed to obtain high resistance to the fluencia: components for plants of cycle combined, thermal sensors conventional, plants of incineration and solar. The most typical steels are the P11, P22, P5, P91 containing different quantities of Cr and Mo (Figure 7). They exist limitations regarding the utilisation of the consumables tubular in these applications, for example, because of the no acceptance generalised of processes FCAW and the low impacts obtained after thermal sensors treatments in the case of tubular threads type rutile.

Apart from the previously commented applications (typical for steel of low alloy or no aleados), exist other a lot of applications more for the tubular threads containing a high percentage of elements of alloy (Cr, Neither, etc), already are stainless steels, basic alloys nickel, in the chemical sectors, petrochemical, repair and maintenance.