Elimination and determination of phosphate

Phosphate in water: origin and elimination
Phosphorus compounds are nutrients for the plants and lead to the growth of algae in surface waters. Depending on the concentration of phosphate in the water, eutrophication can occur. Only 1 gram of fosfato-fósforo (PO4- P) causes the growth of up to 100 g of algae. When these algae die, the processes of decomposition resulting demand of oxygen around 150 grams. The critical concentration for an incipient eutrophication are between 0, 1-0, 2 mg/l PO4- P in tap water and 0, 005-0, 01 mg/l PO4- P in calm waters. In view of the potential danger to surface waters, the directive EU 91/271/EEC specifies values limit for disposal of compounds of phosphate to receiving waters. Depending on the size of the WWTP, these values are 2 mg/l total P (10,000-100,000 h-e) or 1 mg/l total P (> 100,000 h-e).
Where does the phosphate?
Compounds of phosphate which are in the sewage or are discharged directly to surface waters come from:
- Deleted fertilizers in the soil by water or wind
- Human excretions and animals
- Detergents and cleaning products
The burden of total phosphate consists of orthophosphate + Polyphosphate + composed of organic phosphorus, being usually the proportion of orthophosphate the highest.
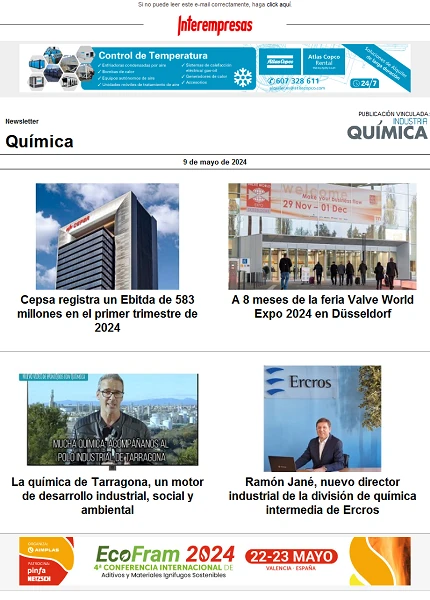
Phosphates there are dissolved, colloidal or solid form. Before performing an analysis, therefore, it is important to consider what kind of phosphates shall determine. If it is only to determine orthophosphate (e.g. for the control of precipitation of phosphorus), only there to filter the sample before analyzing it. However, if it is to determine the concentration of total phosphorus (e.g. for the control of the limit values), first must mix the sample and then to hydrolyzed (subject to digestion).

Elimination of phosphate
Today, it cannot be assumed that the average concentration in the entrance to a municipal sewage treatment plant is 9 milligrams of phosphorus in total. This concentration must be reduced, during the process of residual water treatment, up to the value in the output limit legally specified. There are two ways to do this: the biological removal of phosphorus or the chemical precipitation of phosphate. The disadvantages associated with precipitation methods are the increase in the salinity of the residual water (and therefore also of the receiving water) and the constant rise in the price of the precipitating. In addition, precipitate phosphate salts leads to the increase in the volume of sludge. That is why in practice a combination of biological and chemical removal of phosphorus is used to minimize the consumption of precipitating.
Biological removal of phosphorus
Storage of more phosphate of the normally required in the floculado active mud. This occurs when the mud is an aerobic sometimes environment and sometimes anaerobic (oxygen input enabled / disabled). The effective biological removal of phosphorus is dependent on the presence of sufficient easily biodegradable Organics (BOD5). A relation P/BOD5 < 0.03 and a relationship N/BOD5 of ≪ 0.25 in the entrance to the aeration tank favour the increase of the biological degradation of phosphorus.
Chemical precipitation of phosphate
Orthophosphate compounds are precipitated as phosphates of hardly soluble metals with the help of chemicals (salts of iron or aluminum, grout of lime). The salts are sedimentan and remain in the mud of sewage. The precipitating you can add during primary treatment (pre-precipitación) or the tank ventilation (simultaneous precipitation), or an additional reaction tank below the tank ventilation (postprecipitación). The most widely used method is the simultaneous precipitation, because that is the most economical Variant.
Analysis of phosphate
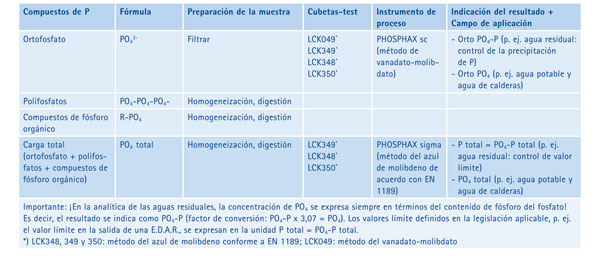
For the control and verification of the Elimination of P and control the limit values are needed periodic analyses on several points of measurement of the residual water treatment process. Furthermore, the selective addition of precipitating phosphorus burden can lead to cost savings. The determination of PO4- P can be conducted in the laboratory with a bucket-test or continuous through an instrument of measurement of process. As a general rule, temporary curves, (eg. for a period of 24 hours) are recorded at a single point of measurement, in order to obtain an accurate view of the magnitude of the burden of PO4. The necessary addition of precipitating can then regularly on the basis of the curve (see Figure 1). More effective is the measure continuous of the concentration of PO4- P with a direct connection to precipitating dispensing systems.
Causes of high concentrations of PO4-P in the effluent, and remedies
Causes and possible solutions:
- You are adding very little precipitating, or it is adding in an unfavorable point: control the addition of precipitating and increase the amount to add or add the precipitating another point
- Phosphorus is redisolviendo in the secondary decanter: the concentration of Ortho PO4- P at the output of the secondary Decanter is higher than in the stage of nitrification and has to increase the oxygen content in the stage of nitrification or improve the mud of recirculation ratio.

Causes and possible solutions:
- Too high proportion of solids, caused by the loss of mud: Floc or structure of light, too small or filamentous activated sludge in combination with hydraulic overloading (rain, snowmelt). It has to control the acid capacity in the aeration tank or measures to combat the non sedimentary mud
- There are polifosfonatos hardly degradable, possibly from industrial cleaning agents: this situation can only be improved through an elimination at the point where it takes place, as the precipitating do not react with such compounds.