Physical separation of purines: a big step for his treatment and environingingmental gestión
Josep Turet, Anna Busquets and Nuria Bruch (SART Medi Ambient of the University of Vic)
25/06/2013Introduction
Perhaps most visible case also occurred in pig farming, in which the estabulaciones "bed" was replaced fairly quickly by the grids, or "eslats" with bottom trench and, in addition, the manual collection of the dejections spent cleaning the stables with pressurized water. This fact led to the emergence of a new type of manure: manure liquid or "slurry", which occurs in large volumes which further aggravate the problem. Anyway, these slurry still, if they are used rationally, ideally suited as fertiliser.
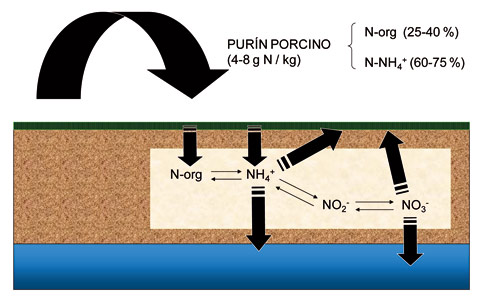
Figure 1: Schema transformations and major destinations usually resulting from the contributions of swine manure on cropland. Decoding: N-org: organic nitrogen, N-NH4+: ammoniacal nitrogen NH4+: ammonium, NO2 : nitrite, NO3 : nitrate.
Technology of treatment
The line of flow of the treatment (Figure 2) chains, an initial reception and homogenization (1) stage, which stores the waste water influent to the treatment (PI), cushioning the variations in the composition and avoiding the sedimentation of solids, and triple separation (2) treatment, resulting in a final effluent that is stored on a raft (3) to be used for fertiirrigacion.
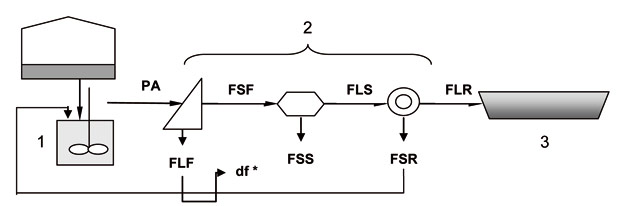
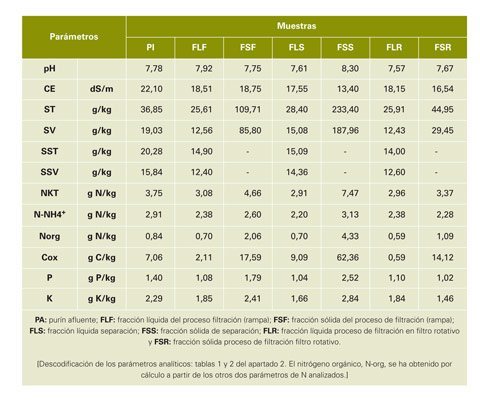
Figure 2: General flowchart of the treatment of separation of fractions studied. Decoding: 1: deposit receipt and homogenization, 2: multiple treatment process, 3: raft for effluent, FR: filtro-rampa, SP: pressure, Rseparator: Rotary filter, PI: influent slurry treatment, FLF: liquid fraction of the filtro-rampa, FSF: solid fraction of filtro-rampa, FLS: liquid fraction of the separator's pressure, FSS: solid fraction of separator pressure, FLR: liquid fraction of the Rotary filter, FSR: solid fraction of Rotary filter and df *: optional destination of the liquid fraction (the Rotary filter or field).




Treatment works seasonally as the manure management requires it. The flow of treatment for this study was approximately 45 m3h.
Methodology of the essay
Splitting of the plant in operation continued, realizar an integrated sampling for each one of the substrates of entrance and exit of the different technological elements of the system of treatment. The intervals of time for the taking of the submuestras integradoras of the final samples were of 30 minutes roughly during a global time of the essay of 3 hours.
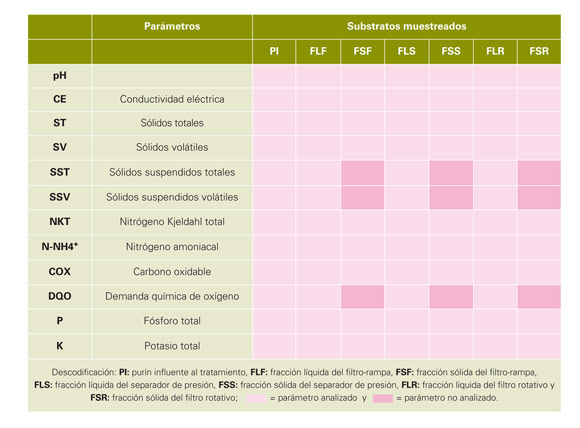
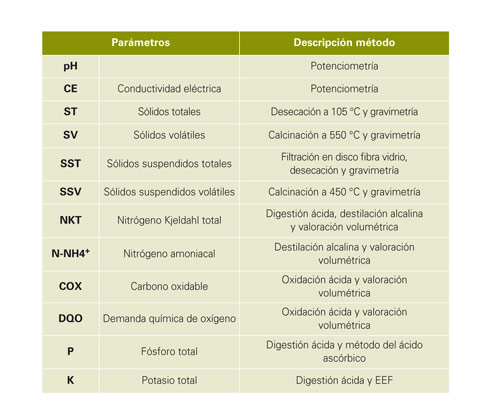
The different samples obtained moved in isothermal sensors container to the Laboratories SART of the University of Vic (Barcelona) and stored in conditions of refrigeration for the realisation of all the analytical determinations programmed. The types of substrates muestreados and the determinate analytical parameters come exposed in the table 1.
The analytical methodologies used (table 2), have been the standard for this type of samples and have been based in the ' Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater' [APHA, AWWA, WEF, 1995].
Results
The influent slurry
Results from other analytical parameters, whereas the effects relating to the conditions expressed in the previous paragraph, correspond perfectly to the normal characteristics of liquid swine manure of bait (SART Medi Ambient, 2013).
Filtration on ramp
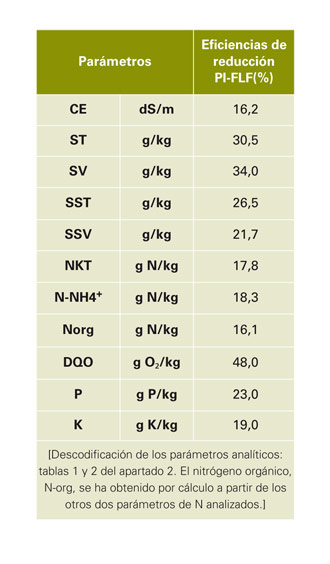
Obviously, the interest of a swine farm surplus in cattle manure on the requirements of the agricultural fields that have fundamentally lies in reduce phytonutrients and thus achieve a rational fertilization, and, currently, especially in nitrogen. The results obtained in this element are not as spectacular as in other parameters, but interesting, since close to 18% efficiencies mean that exploitation, managing export solid fraction obtained, reduces most of the useful agricultural surface ratios you need for these cattle manure (see paragraph 4 yields). Also 23 and 19% reduction efficiencies are should highlight to the P and K, respectively.
Treatment with pressure separator
The separator filter with pressing (Figure 5) system is ideal, in general, to obtain solid fractions of high concentration and can be used in the treatment of slurry and manure, both different types of very wet solid fractions. The latter case is now occupied us, the solid fraction obtained from the filtro-rampa (FSF) treatment, although we can serve to visualize the effect of this separator system in general.
The results of this process are presented in table 3, from which the reduction efficiencies set out in table 5 are calculated, and in addition, the following conclusions are obtained:
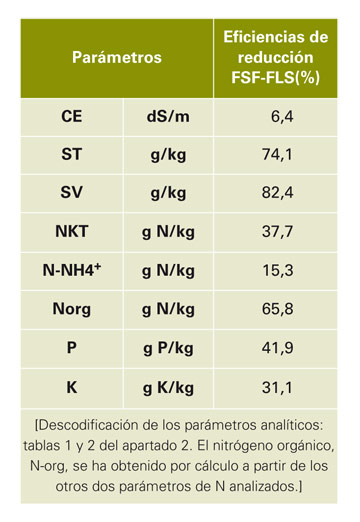
- The separator solids handling of a solid fraction to get another more concentrated has shown very good results, since the efficiencies of reduction on the entry (FSF) substrate, whereas the resulting liquid fraction (FLS) have been high (about 74 and 82% for the ST and SV, respectively).
- The solid fraction obtained (FSS) shows characteristics in concentration of solids (23% WT/WT) making it manageable and stackable for storage or for composting. It has more than doubled the concentration of solids from influent material, as well as other parameters (such as phosphorus).
- You get a liquid fraction (FLS) of similar characteristics (with similar charges) to the resulting from the filtro-rampa, so that you can mix without any prejudice for use or treatment.
Treatment with rotary filter
The results achieved are those set out in table 3 (FLR and FSR), but Mission of this article is not evaluative analysis of this particular and specific process of exploitation that has this facility.
Aspects to be noted by way of conclusions
It should, finally, to combine the data of different treatments to obtain final definitive visions. So the two points that follow are:
I. the visualization of the effects obtained in liquid fractions or liquid effluents resulting from the three types of tested separators, in relation to the treated manure, are presenting the figures that follow (figures 7, 8 and 9). The obtained liquid effluents are very similar each other, result that allows, according to the objectives to be pursued, the selection of unique treatments or, as is the case of our experimental exploitation, varying combinations with subsequent mixture of liquid effluents.
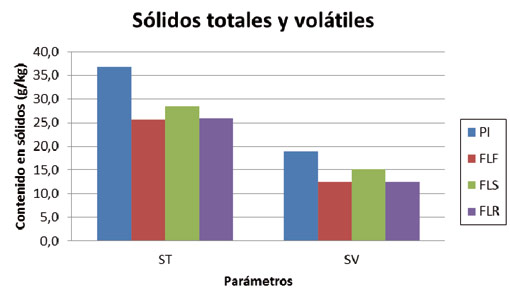
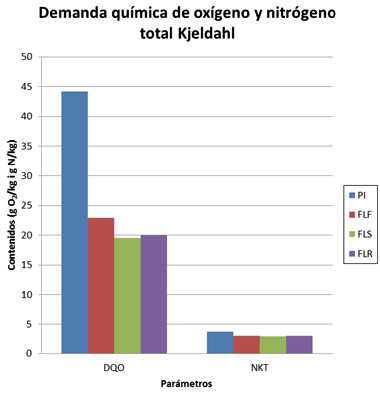
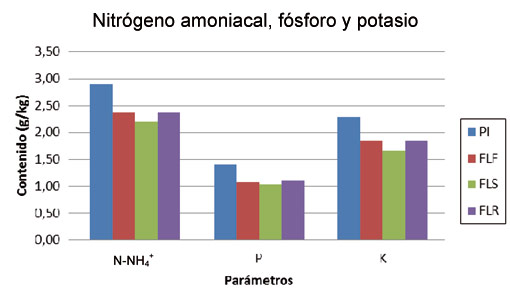
Figure 9. General histogram of content in ammoniacal nitrogen (N-NH4+), total phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) tributary treated manure (PI) and the different effluents (liquid fractions) obtained in each treatment: FLF for filtration in ramp, FLS for separator's pressure and FLR Rotary filter.
The questions that do us immediately in front of one of these processes of physical separation refer to the degree of purification that provide us like pre-treatments. The figure 8 sample the comparative of the chemical demand of oxigeno (DQO) and the total nitrogen Kjeldahl (NKT). It is notorious that, if we compare the liquid fractions with the purín influente of which come from, the reduction in DQO is very high, near to 50% of the initial content. By his part, the N has suffered a relatively lower variation in his concentration of these liquid fractions with regard to the one of the purín, so that only they can use values of next reduction to the 15-20%.
Is essential to refer also to the nutrients for the vegetal crops (the fitonutrientes) and especially to which need of majority form (the macronutrientes): N, P and K. Considering those that will have a relatively fast effect on the vegetables, the N-amoniacal (N-NH4+) and good part of the P and the K in the purines, the figure 9 sample that the three fitonutrientes conserve mostly in the liquid fractions obtained, and that his reductions with regard to the purín tributary situate between a 18 and 23% (can generalise in 15-25%) and the greater retention always produces in the P.
If it thinks in the liquid fractions like fertilizantes liquid, the relations between the macronutrientes in N (in NKT):P:K would situate near of 3,0:1,0:1,8.
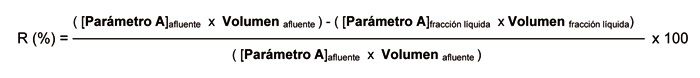
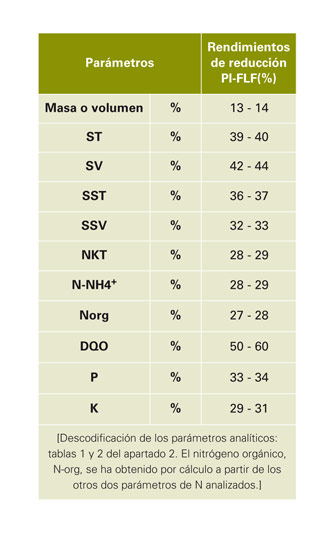
II. not only are interested in liquid fractions concentration reduction efficiency obtained, but that, considering the volumes distributed between the two fractions, are fundamental to management in livestock treatments reducing yields. The mathematical expression for these reduction yields is:
Bibliography used and complementary
-Auger, r., Turet, j., Busquets, a., Farrés, M., Font, x. & Sánchez, a. (2011). Respirometric screening of several types of manure and mixtures intended for composting. Bioresource Technology, 102: 1367-1377
-DAAM (2013). Statistics Metropolità. http://www20.gencat.cat/portal/site/DAR/ Departament D'agricultura, Ramaderia, fishing, Alimentació i Medi Natural (Generalitat de Catalunya).
-DARP (1998). CODI de bones pràctiques agràries in relació amb the nitrogen. Order of 22 October 1998. Departament D'agricultura, Ramaderia i fishing. Diari Oficial de la Generalitat de Catalunya.
-Espona, j., Turet, j. and Viver, j. (1995). Forced aeration of pig manure in semi-continuous regime. Water technology, 141: 41-45.
-García, M. (1997). Characterization of the puri porci in comarca D'osona granges: influence of gastroenteroloy i of the consumit pins. Final career project. VIC: Escola Politècnica Superior. Universitat de Vic.
MAGRAMA-Secretary General technique (2013). Surveys livestock, analysis of the number of animals by types. www.magrama.gob.es/ca/ Ministry of agriculture, food i environment (Government of Spain).
-Pomar, j. (1984). Study of the behavior and evolution of mineral nitrogen from swine liquid manure into the soil and its availability for crops. Doctoral thesis. Lleida: Escola technique Superior D'enginyers Agronoms. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya.
-Sana, j., Casas, C., Espona, j. Vinyeta, e. (1998). Study of the ability of purins personnel dels comarca D'osona sols d' assimilació. "Comprehensive Pla per a la Gestió dels purins comarca D'osona personnel". ASSAPORC.
-SART Medi Ambient (2013). Résultats analitics propis. Servei d' advice, research and applied technology (SART). Universitat de Vic (Vic).
-Turet, j. (1984). Aprofitament de residus agropecuaris: digestio metanogenica de residus personnel. Butll. Soc. Cat. One hundred., 2 (3): 101-108.
-Turet, j., Espona, j. Serra, x. (1992). Review dels estudis developed from the "Pla pilot per a la Gestió dels purins comarca D'osona personnel". Servei d'Assaigs i research technology (SART) of the Universitat de Vic - Consell Comarcal D'osona.
-Turet, j. i Vilalta, e. (1997). Memory of the "Pla d'estudi i Gestió dels purins personnel of Les Masies de Voltregà". Servei d'Assaigs i research technology (SART) of the Universitat de Vic - Ajuntament de Les Masies de Voltregà.
-Vilalta, e. (1993). Estudi dels efectes dels coadjuvants in the residuals d'Aigues depuració microbiologics. Final career project. VIC: Escola Universitària Politècnica D'osona. Estudis Universitaris in Vic.
-Vilalta, e., Turet, j., Costa, C. Terradellas, o. (1999). Study of the ramaderia D'osona. "Comprehensive Pla per a la Gestió dels purins comarca D'osona personnel". ASSAPORC.
-Vineyards, j. (1998). Experimental Estudi metanogenica dels purins personnel i digestio comparatiu de les seves fraccions solid liquid i. Final career project. VIC: Escola Politècnica Superior. Universitat de Vic.